How To Install SpaceWalk on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Spacewalk is an open-source package and system management solution for RedHat derivative distributions like CentOS, Scientific Linux and Fedora, developed by the spacewalk community.
The Spacewalk is the upstream project for the source of Red Hat Satellite, released under GPLv2 license.
Spacewalk provides the web interface to manage and view the updates for the system that are registered with Spacewalk, and we can initiate the task such as install, update, inventory, and so on.
Article Series:
1: How to Install SpaceWalk on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
2: Managing Channels and Repositories in Spacewalk
3: Register clients with SpaceWalk Server
Here is the tutorial about installing Spacewalk on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
Features
- Inventory of the systems
- Install and Update system packages.
- Perform a Kick-start installation.
- Deploy and Manage the configuration files from a single location
- Start / Stop / Configure the guests.
- Distribute the content across the multiple Geographical location using spacewalk proxy.
Requirements
- Outbound open ports 80, 443
- Inbound open ports 80, 443, 5222 (only if you want to push actions to client machines) and 5269 (only for push actions to a Spacewalk Proxy), 69 udp if you want to use tftp
- Storage for the database: 250 KiB per client system + 500 KiB per channel + 230 KiB per package in a channel (i.e., 1.1GiB for a channel with 5000 packages)
- Storage for packages (default /var/satellite): Depends on what you’re storing; Red Hat recommend 6GB per channel for their channels
- 2GB RAM minimum, 4GB recommended
- Underlying (SpaceWalk Server) OS is fully up-to-date.
Environment
HostName: server.itzgeek.local
IP Address: 192.168.1.10
OS: CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core)
Make sure the system is configured with static IP Address.
READ: How to Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Prerequisites
Setup Repositories
Before installing Spacewalk on CentOS, we must configure the required repositories on our system.
Install the Spacewalk repository rpm to get the latest version of Spacewalk version.
yum install -y yum-plugin-tmprepo yum install -y spacewalk-repo --tmprepo=https://copr-be.cloud.fedoraproject.org/results/%40spacewalkproject/spacewalk-2.9/epel-7-x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml --nogpg
Also, set up EPEL repo on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Additionally, in RHEL 7, subscribe the system to Optional Channels.
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
Hostname
Your Spacewalk server should have a resolvable fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) like hostname.domain.com.
To do that, edit /etc/hosts file.
vi /etc/hosts
Modify it according to your environment.
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 # Your Spacewalk Server 192.168.1.10 server.itzgeek.local server
Firewall
As said in the prerequisites, we need to have the outbound port opened. Run the following on terminal to allow the required ports.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Add port 5222 if you want to push actions to client machines and 5269 for push actions to a Spacewalk Proxy, 69 udp if you want to use tftp.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5222/tcp --add-port=5269/tcp --add-port=69/udp
Restart firewall service using the command:
firewall-cmd --reload
SpaceWalk Database
SpaceWalk supports PostgreSQL (version 8.4 or higher) or Oracle ( version 10g or higher) as a database for storing its data.
Embedded Database
Spacewalk has the embedded setup for PostgreSQL database which will do the automatic Spacewalk installation without having user intervention to enter the database information.
Embedded database method is very easy to setup and runs the Spacewalk in no time; this is very useful for those who do not have any database knowledge. Here, we will use the embedded database for Spacewalk installation.
yum -y install spacewalk-setup-postgresql
External Database
You can use the external PostgreSQL or Oracle database to install Spacewalk. You can find the tons of documents online to setup database.
Install SpaceWalk
If you prefer to use the PostgreSQL database (Either Embedded or External PostgreSQL database), then install the following package.
yum install -y spacewalk-postgresql
Configure SpaceWalk
If you have installed the embedded database, then use below command. It will ask you to enter the admin mail and organization details to generate the self-signed certificate for secure access.
spacewalk-setup
Output:
* Setting up SELinux.. ** Database: Setting up database connection for PostgreSQL backend. Database "rhnschema" does not exist ** Database: Installing the database: ** Database: This is a long process that is logged in: ** Database: /var/log/rhn/install_db.log *** Progress: ### ** Database: Installation complete. ** Database: Populating database. *** Progress: ########################## * Configuring tomcat. * Setting up users and groups. ** GPG: Initializing GPG and importing key. ** GPG: Creating /root/.gnupg directory You must enter an email address. Admin Email Address? [email protected] * Performing initial configuration. * Configuring apache SSL virtual host. Should setup configure apache's default ssl server for you (saves original ssl.conf) [Y]? Y << Press Y ** /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf has been backed up to ssl.conf-swsave * Configuring jabberd. * Creating SSL certificates. CA certificate password? << Enter Certificate Password Re-enter CA certificate password? << Re Enter Certificate Password Cname alias of the machine (comma seperated)? server.itzgeek.local,server << Certificate Subject Name (Your Domain Name) Organization? ITzGeek << Your Organization Name Organization Unit [server.itzgeek.local]? IT << Your Organization Unit Email Address [[email protected]]? << Email Address City? Albany << Your City State? NY << Your State # Country code (Examples: "US", "JP", "IN", or type "?" to see a list)? US << Your Country ** SSL: Generating CA certificate. ** SSL: Deploying CA certificate. ** SSL: Generating server certificate. ** SSL: Storing SSL certificates. * Deploying configuration files. * Update configuration in database. * Setting up Cobbler.. Cobbler requires tftp and xinetd services be turned on for PXE provisioning functionality. Enable these services [Y]? Y << Press Y * Restarting services. Installation complete. Visit https://server.itzgeek.local to create the Spacewalk administrator account.
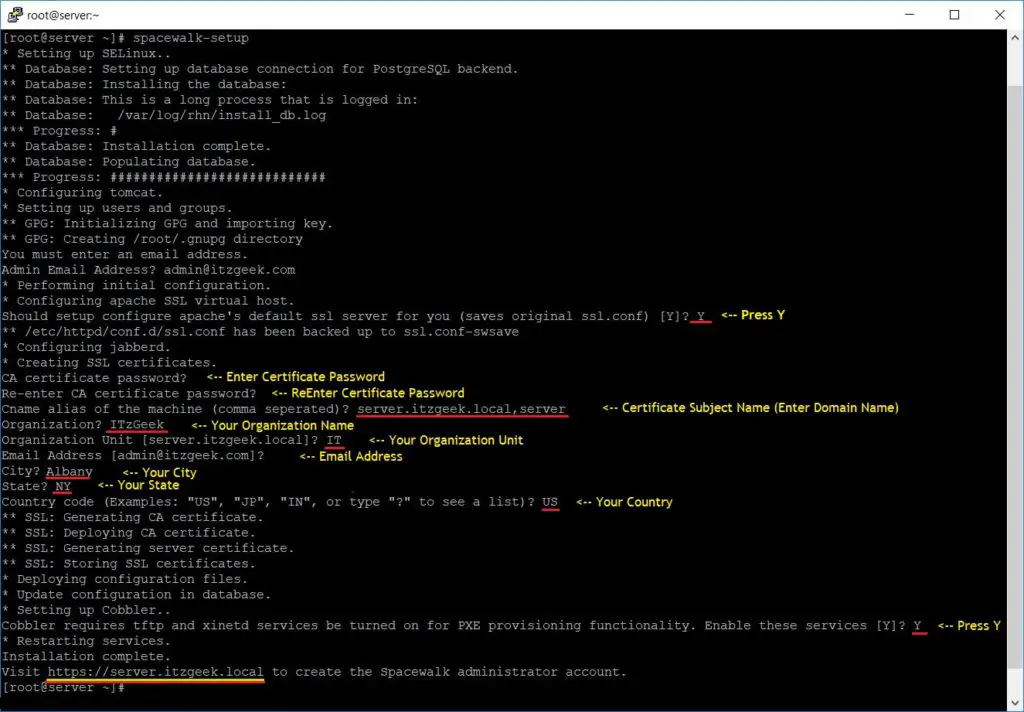
Once the installation is complete, check the status of Spacewalk service.
/usr/sbin/spacewalk-service status
You can start the Spacewalk services manually if not started automatically.
/usr/sbin/spacewalk-service start
Access Spacewalk
Open up your browser and navigate it to below URL.
OR
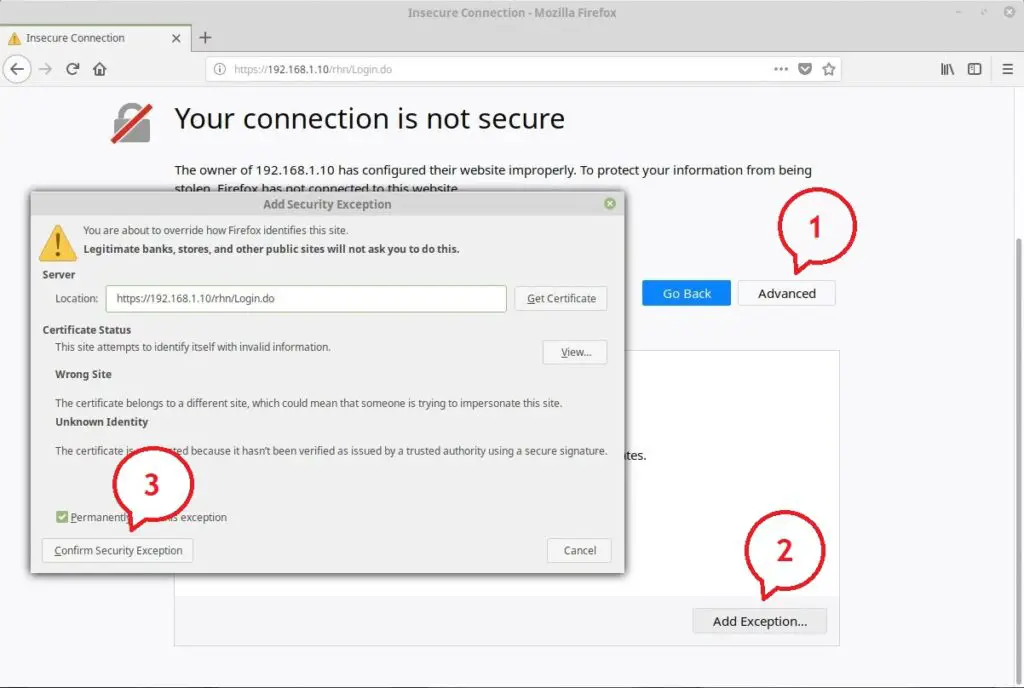
You need to add exceptions for the self-signed certificate.
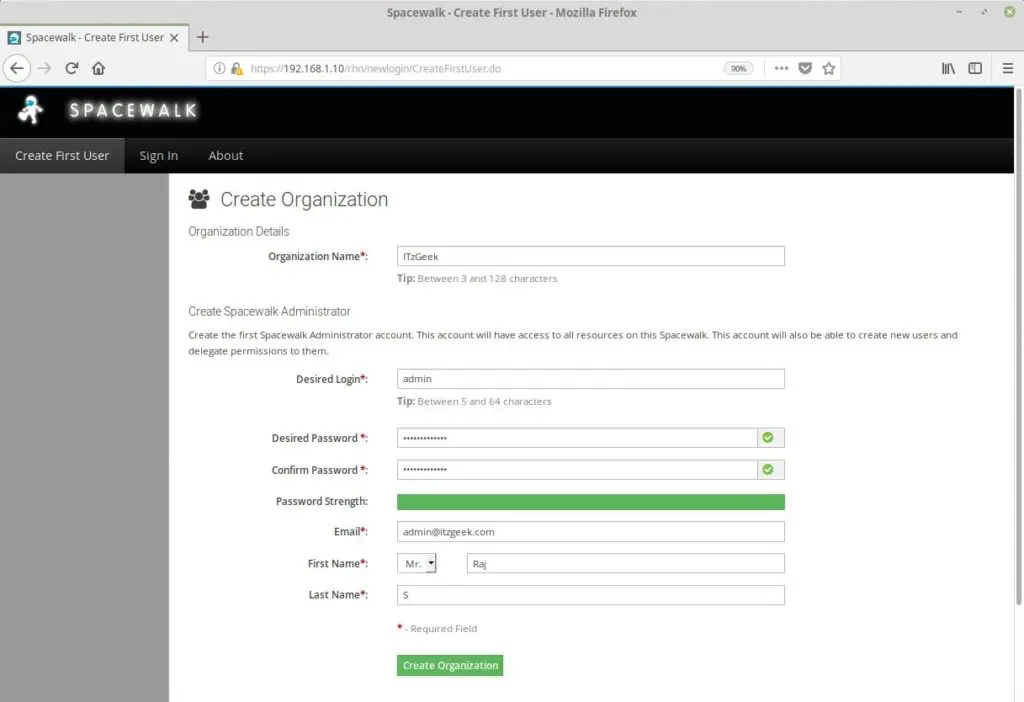
You will be asked to create an administrator account for the spacewalk. Fill up details and then click on Create Organization.
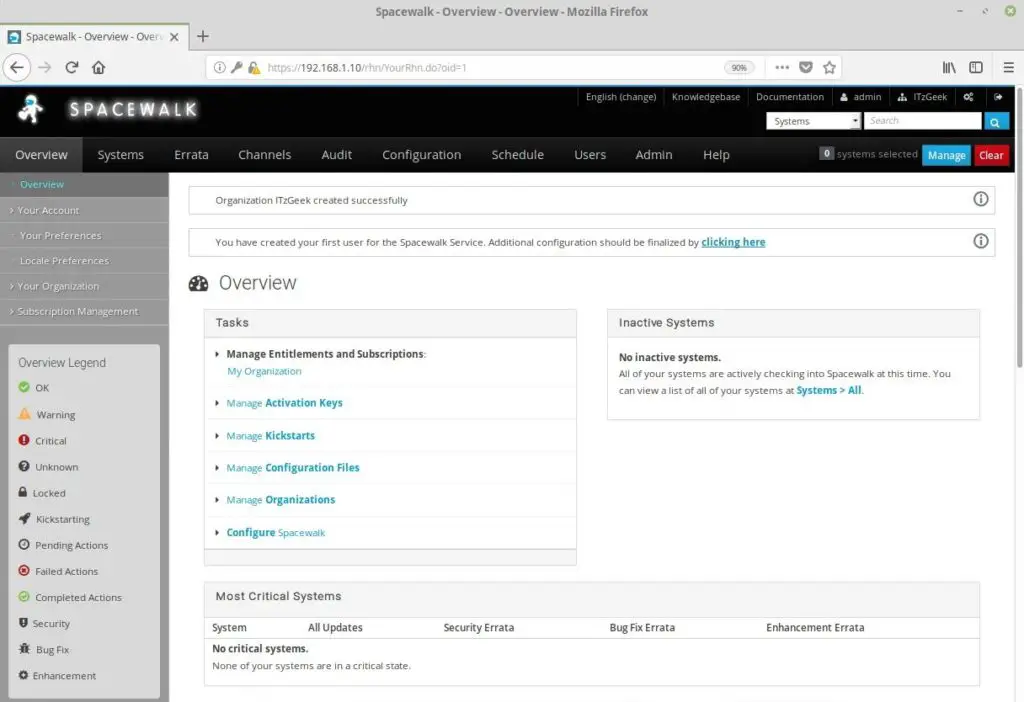
Upon successful creation of the administrator account, it will take you to the home page of spacewalk where you can do all the administrative activities.
Conclusion
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to install Spacewalk on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7. In our next tutorial, we will configure the SpaceWalk to distribute the updates for CentOS clients.
