How To Install Foreman on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 / Oracle Linux 7
Foreman is an open source tool that helps you to provision, configure, manage and monitor the servers. With the help of configuration management tools such as Puppet, Chef, Salt, and Foreman’s smart proxy architecture, you can easily automate repetitive tasks, quickly deploy applications, and proactively manage change.
Foreman provides comprehensive, interaction facilities including a web frontend, CLI and RESTful API which enables you to do the above tasks, supports both on-premise with VMs and bare-metal or in the cloud.
With Foreman, we can manage 10s to 10,000s of physical or virtual servers via a web browser.
Features
- Discover, provision and upgrade your entire bare-metal infrastructure
- Create and manage instances across private and public clouds
- Group your hosts and manage them in bulk, regardless of location
- Review historical changes for auditing or troubleshooting
- Extend as needed via a robust plugin architecture
- Automatically build images (on each platform) per system definition to optimize deployment
It can provision systems on bare metal (physical) as well as the following cloud providers,
- Amazon EC2
- Google Compute Engine
- Libvirt
- OpenStack
- oVirt and RHEV
- Rackspace
- VMware
System Requirements
Supported Platforms
Foreman can be installed on following operating systems,
- RHEL / CentOS / Fedora / Oracle Linux
- Ubuntu / Debian
- Solaris 8, 10
- OpenSUSE / SLES
- CoreOS
- FreeBSD
- Junos
Hardware Requirements
- 4GB RAM
- 2GB HDD Disk Space
Prerequisites
Before installing Foreman, make sure you have set up an FQDN for your server.
vi /etc/hosts
Make an entry, like this.
192.168.1.10 server.itzgeek.local server
Also, do not forget to setup the valid hostname for the above host entry.
hostnamectl set-hostname server.itzgeek.local
Install Foreman on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Foreman can be installed in different methods. The recommended way is with the puppet-based Foreman Installer, but you may also use your distribution’s package manager or install directly from the source.
The Foreman installer is a collection of Puppet modules that install everything required for a full working Foreman setup. It uses native OS packaging (e.g., RPM packages) and adds necessary configuration for the complete installation.
The Foreman installer will install the necessary components such as the Foreman web UI, Smart Proxy, Passenger (for the puppet master and Foreman itself), and optionally TFTP, DNS and DHCP servers.
First, configure EPEL, Puppet and Foreman repositories.
rpm -ivh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppet5/puppet5-release-el-7.noarch.rpm rpm -ivh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm rpm -ivh https://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.20/el7/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm
Enable the RHEL Optional repository (RHEL only).
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
Run the following command to download Foreman installer.
yum -y install foreman-installer
Now, run the Foreman installer to start installing Foreman.
foreman-installer
The installation run is non-interactive, but the configuration can be customized by supplying any of the options listed in foreman-installer –help, or by running foreman-installer -i for interactive mode.
Once the installation is completed, you will see an output like below where you would find the initial username and password to access the Foreman.
Installing Done [100%] [................................] Success! * Foreman is running at https://server.itzgeek.local Initial credentials are admin / SdjdyHStak9vrB3r * Foreman Proxy is running at https://server.itzgeek.local:8443 * Puppetmaster is running at port 8140 The full log is at /var/log/foreman-installer/foreman.log
Note down initial username and password, and you would need this for accessing Foreman’s dashboard.
Firewall Configuration
The components of Foreman use the following ports and they need to be allowed in IP tables (FirewallD) / Hardware Firewall.
| Port | Protocol | Required For |
|---|---|---|
| 53 | TCP & UDP | DNS Server |
| 67, 68 | UDP | DHCP Server |
| 69 | UDP | * TFTP Server |
| 80, 443 | TCP | * HTTP & HTTPS access to Foreman web UI – using Apache + Passenger |
| 3000 | TCP | HTTP access to Foreman web UI – using standalone WEBrick service |
| 3306 | TCP | Separate MySQL database |
| 5910 – 5930 | TCP | Server VNC Consoles |
| 5432 | TCP | Separate PostgreSQL database |
| 8140 | TCP | * Puppet Master |
| 8443 | TCP | Smart Proxy, open only to Foreman |
Run following commands to allow above ports in FirewallD.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=53/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=67-69/udp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3000/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5910-5930/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5432/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8140/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8443/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Access Foreman Web Console
Open up your favorite web browser, navigate to
OR
Add an SSL exception in the browser to access the Foreman web console.
Log in with the username and password shown to you at the end of Foreman installation.
Once you logged in, you will get an overview page like below.
It is recommended to change the password of Admin user for security reasons. To do that, click <Username> (Top right) >> My Account.
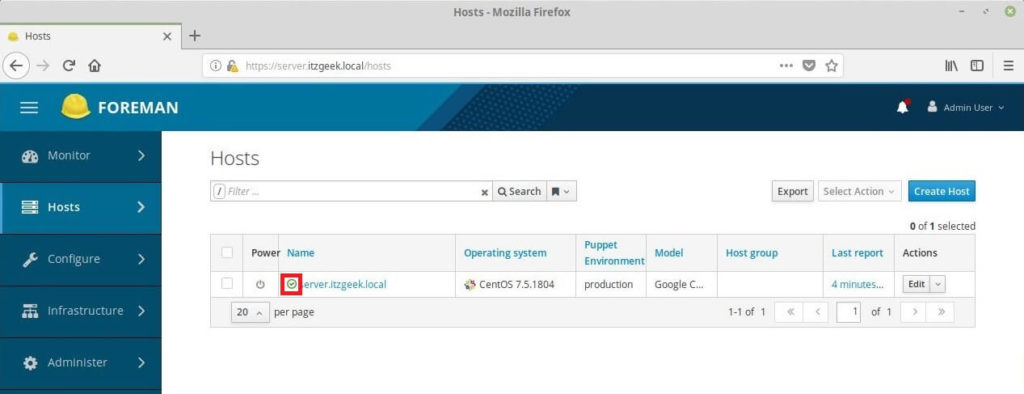
To list down the available hosts, go to Hosts >> All Hosts from Menu.
Configure Foreman (Optional)
If your Foreman host is not visible in Hosts >> All Hosts tab, you should run below command which will send the first Puppet report to Foreman, automatically creating the host in Foreman’s database.
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
Output:
Info: Using configured environment 'production' Info: Retrieving pluginfacts Info: Retrieving plugin Info: Retrieving locales Info: Loading facts Info: Caching catalog for server.itzgeek.local Info: Applying configuration version '1543476534' Notice: Applied catalog in 0.16 seconds
Puppet 3+ may show notice/warning during the first run, and this can be ignored.
Since we do not have any puppet clients, All Hosts tab would only list your Foreman host, with an “O” status and green tick mark. This indicates its status is OK, with no changes made in the last Puppet run.