20 Useful apt, apt-get, and apt-cache Command Examples for Package Management
Advanced Package Tool (APT) is a powerful and free software package-management user interface in Debian based operating systems, including Ubuntu and LinuxMint to handle the installation and removal of software packages.
The apt command has been introduced to merge apt-get and apt-cache into one single command and provide a pleasant experience for end users by efficiently handling packages.
APT was first designed as a front-end for dpkg to work with .deb packages, but it has been modified to also work with Redhat Package Manager (RPM) via APT-RPM.
apt-get is the command line management tool supplied with the apt package (to work with APT) which helps to install new software packages, remove existing software packages, upgrading software packages and also upgrading the operating system to the newer version.
apt-cache is another command line tool which helps you search the available packages for your Debian, Ubuntu, and LinuxMint system. Also, it is used to get the information of software packages. This tool uses the package cache of APT to find packages and package names.
20 apt command examples
With starting from Ubuntu 16.04, Debian 9 and LinuxMint 18, the new apt command is available for you by default.
Most of the examples will have apt and equivalent apt-get or apt-cache commands. So, you can use the equivalent commands on older versions of Debian, Ubuntu, and LinuxMint.
If the machine has the apt package version 1.0 and above the apt command should work just fine.
1. How to install packages with apt
To install a package, you can use the following command. You can mention multiple package names separated by a space.
sudo apt-get install vsftpd
OR
sudo apt install vsftpd
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: vsftpd 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 115 not upgraded. Need to get 115 kB of archives. After this operation, 336 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 vsftpd amd64 3.0.3-3ubuntu2 [115 kB] Fetched 115 kB in 0s (133 kB/s) Preconfiguring packages ... Selecting previously unselected package vsftpd. (Reading database ... 197971 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../vsftpd_3.0.3-3ubuntu2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Processing triggers for systemd (229-4ubuntu21) ... Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-19) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ... Setting up vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Processing triggers for systemd (229-4ubuntu21) ... Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-19) ...
2. How to install .deb package with apt
This option is useful when you have downloaded the packages (see: example 17) on the system for the local installation. Use the apt command with deb subcommand to install the .deb package.
sudo apt deb vsftpd_3.0.3-3ubuntu2_amd64.deb
Output:
Selecting previously unselected package vsftpd. (Reading database ... 198622 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack vsftpd_3.0.3-3ubuntu2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Setting up vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Processing triggers for systemd (229-4ubuntu21) ... Processing triggers for ureadahead (0.100.0-19) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ...
3. How to install specific package version with apt
Though the latest package version available for your system, you can install the specific version of a package by appending the version number after the package name and equal sign.
apt install php=1:7.0+35ubuntu6
OR
apt-get install php=1:7.0+35ubuntu6
You can find the available versions of php for your system, shown like in example 13.
4. How to remove packages with apt
To remove any package with apt, run the following command. You can mention multiple package names separated by a space.
sudo apt remove vsftpd
OR
sudo apt-get remove vsftpd
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages will be REMOVED: vsftpd 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 115 not upgraded. After this operation, 336 kB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y (Reading database ... 198027 files and directories currently installed.) Removing vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ...
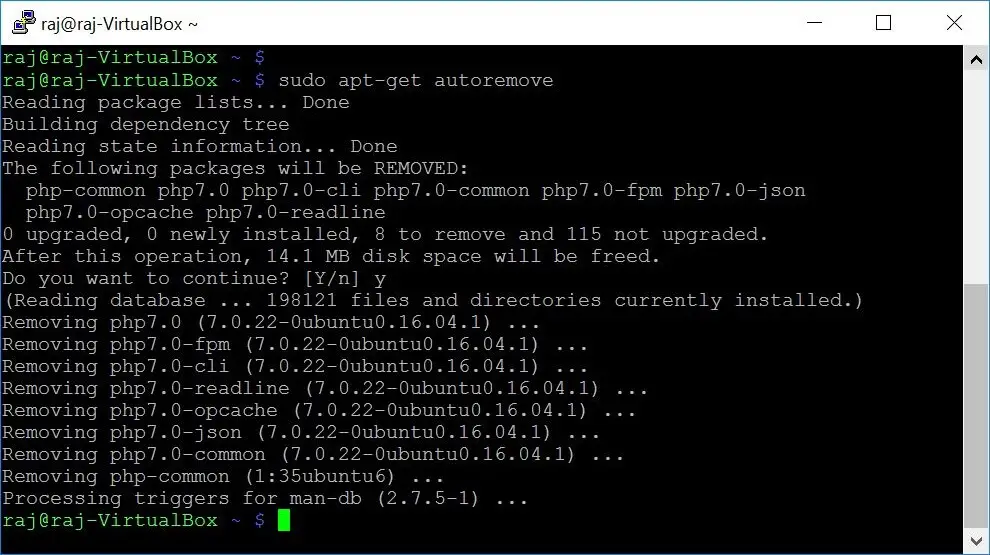
5. How to remove unused packages with apt
Using an option autoremove with the apt command will remove all unused packages from your system which are no longer needed.
sudo apt autoremove
OR
sudo apt-get autoremove
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages will be REMOVED: php-common php7.0 php7.0-cli php7.0-common php7.0-fpm php7.0-json php7.0-opcache php7.0-readline 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 8 to remove and 115 not upgraded. After this operation, 14.1 MB disk space will be freed. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y (Reading database ... 198121 files and directories currently installed.) Removing php7.0 (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-fpm (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-cli (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-readline (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-opcache (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-json (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php7.0-common (7.0.22-0ubuntu0.16.04.1) ... Removing php-common (1:35ubuntu6) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ...
6. How to completely remove packages with apt
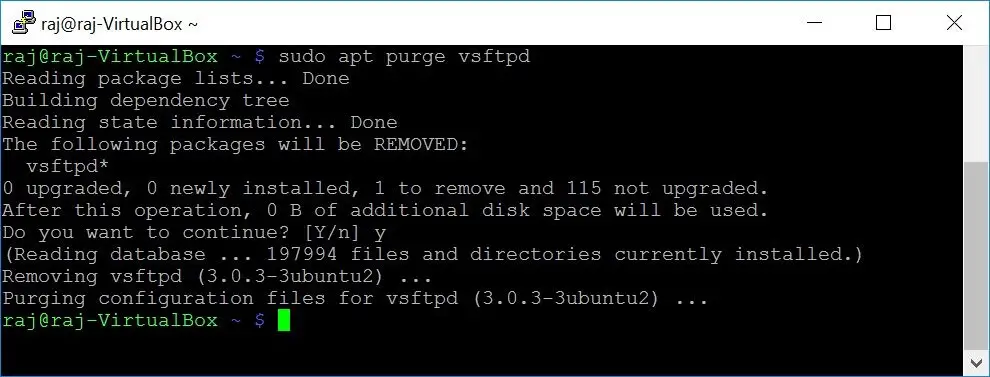
Both apt remove and apt autoremove commands will leave user modified configuration by default when the packages are removed for future installation. However, you can completely remove those leftover files by using the purge command.
sudo apt purge vsftpd
OR
sudo apt-get purge vsftpd
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages will be REMOVED: vsftpd* 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 to remove and 115 not upgraded. After this operation, 0 B of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y (Reading database ... 197994 files and directories currently installed.) Removing vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ... Purging configuration files for vsftpd (3.0.3-3ubuntu2) ...
7. How to update the local repository Index with apt
The update command downloads the package indexes which have up-to-date information about the new and updated packages that are available from locations specified in /etc/apt/sources.list.
This command should always be run before an upgrade or a full-upgrade command.
sudo apt update
OR
sudo apt-get update
Output:
Hit:1 https://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security InRelease Hit:2 https://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial InRelease Hit:3 https://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates InRelease Hit:4 https://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu xenial InRelease Hit:5 https://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports InRelease Ign:6 https://packages.linuxmint.com sylvia InRelease Hit:7 https://packages.linuxmint.com sylvia Release Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done
8. How to find updates with apt command
You can use the --upgradable to get to know what are the updates available for your system. The command will list packages with the new version available for the system and the current version.
sudo apt list --upgradable
Output:
Listing... Done apparmor/xenial-updates 2.10.95-0ubuntu2.8 amd64 [upgradable from: 2.10.95-0ubuntu2.7] apport/xenial-updates,xenial-updates,xenial-security,xenial-security 2.20.1-0ubuntu2.15 all [upgradable from: 2.20.1-0ubuntu2.10] apt/xenial-updates 1.2.25 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.2.24] apt-transport-https/xenial-updates 1.2.25 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.2.24] apt-utils/xenial-updates 1.2.25 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.2.24] archdetect-deb/xenial-updates 1.117ubuntu2.3 amd64 [upgradable from: 1.117ubuntu2.2] bind9-host/xenial-updates,xenial-security 1:9.10.3.dfsg.P4-8ubuntu1.10 amd64 [upgradable from: 1:9.10.3.dfsg.P4-8ubuntu1.8] binutils/xenial-updates,xenial-security 2.26.1-1ubuntu1~16.04.6 amd64 [upgradable from: 2.26.1-1ubuntu1~16.04.5]
9. How to upgrade packages with apt
To upgrade all the installed packages on your system, you can use the upgrade command. Under no circumstances, currently installed packages are not removed or packages which are not already installed retrieved and installed for meeting dependencies.
sudo apt upgrade
OR
sudo apt-get upgrade
10. How to upgrade full system with apt
The dist-upgrade command let us upgrade the whole system similar to upgrade command, but it has smart conflict resolution system that intelligently handles changing dependencies with new versions of packages which means the command may remove or install some packages to meet dependency.
sudo apt full-upgrade
OR
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
11. How to upgrade specific packages with apt
Sometimes, you may need to upgrade only one or few packages, and in this situation, you can use --only-upgrade to upgrade specific packages.
Note: --only-upgrade is option designed only to upgrade the existing packages; it does not install new packages.
sudo apt-get install --only-upgrade openssl
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following packages will be upgraded: openssl 1 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 263 not upgraded. Need to get 492 kB of archives. After this operation, 0 B of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/main amd64 openssl amd64 1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10 [492 kB] Fetched 492 kB in 1s (405 kB/s) (Reading database ... 197991 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../openssl_1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openssl (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10) over (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.8) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ... Setting up openssl (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10) ...
12. How to reinstall packages with apt
Using sub --resinstall command with install command, you can reinstall deb packages to resolve any installation issues.
Note: --reinstall will only install the newest version of the software package.
sudo apt install --reinstall openssl
OR
sudo apt-get install --reinstall openssl
Output:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 1 reinstalled, 0 to remove and 263 not upgraded. Need to get 0 B/492 kB of archives. After this operation, 0 B of additional disk space will be used. (Reading database ... 197991 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../openssl_1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openssl (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10) over (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.7.5-1) ... Setting up openssl (1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10) ...
13. How to list all packages with apt
The list command will help you identify whether the software package is already installed or available for your system.
The output will have the word “Installed” if the package is already installed. In case it is not already installed, the output will have the name and package version.
Installed
sudo apt list openssl
Output:
Listing... Done openssl/xenial-updates,xenial-security,now 1.0.2g-1ubuntu4.10 amd64 [installed]
Available
sudo apt list vsftpd
Output:
Listing... Done apache2/xenial-updates,xenial-security 2.4.18-2ubuntu3.5 amd64
14. How to list all installed packages with apt
If you want to get only the list of installed software packages on the system, then use the below command.
apt list --installed
Output:
Listing... accountsservice/xenial-updates,now 0.6.40-2ubuntu11.3 amd64 [installed] acl/xenial,now 2.2.52-3 amd64 [installed] acpi-support/xenial,now 0.142 amd64 [installed] acpid/xenial,now 1:2.0.26-1ubuntu2 amd64 [installed] . . . . . . zenity-common/xenial,xenial,now 3.18.1.1-1ubuntu2 all [installed] zip/xenial,now 3.0-11 amd64 [installed] zlib1g/xenial-updates,now 1:1.2.8.dfsg-2ubuntu4.1 amd64 [installed]
15. How to list all available versions of packages with apt
You can use the below sub --all-versions command to get a list of all available versions of a package. Let us check all versions of PHP package.
apt list --all-versions php
Output:
Listing... Done php/xenial-updates,xenial-updates 1:7.0+35ubuntu6.1 all php/xenial,xenial 1:7.0+35ubuntu6 all
16. How to Find / Search packages with apt
You can use the search command to search for a particular package. The command will simply list all packages that contain given phrase.
sudo apt search vsftpd
OR
sudo apt-cache search vsftpd
Output:
p vsftpd - lightweight, efficient FTP server written for security p vsftpd:i386 - lightweight, efficient FTP server written for security p vsftpd-dbg - lightweight, efficient FTP server written for security (debug) p vsftpd-dbg:i386 - lightweight, efficient FTP server written for security (debug)
17. How to get information about a package with apt
To know more about a particular package, use the following command.
sudo apt show vsftpd
OR
sudo apt-cache show vsftpd
Output:
Package: vsftpd Priority: extra Section: net Installed-Size: 328 Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <[email protected]> Original-Maintainer: Jörg Frings-Fürst <[email protected]> Architecture: amd64 Version: 3.0.3-3ubuntu2 Replaces: ftp-server Provides: ftp-server Depends: debconf (>= 0.5) | debconf-2.0, init-system-helpers (>= 1.18~), libc6 (>= 2.15), libcap2 (>= 1:2.10), libpam0g (>= 0.99.7.1), libssl1.0.0 (>= 1.0.0), libwrap0 (>= 7.6-4~), adduser, libpam-modules, netbase Recommends: logrotate, ssl-cert Conflicts: ftp-server Filename: pool/main/v/vsftpd/vsftpd_3.0.3-3ubuntu2_amd64.deb Size: 115492 MD5sum: c0c62c32c75eea6a4d36e91b8695453b SHA1: b97efcd25ed49537f0601b3687f39b07e126c0c0 SHA256: c1d07ecf1e8fd72714f0cc803498a59c9b6a88168ed340e9560e7e904d6bfc18 Description-en: lightweight, efficient FTP server written for security This package provides the "Very Secure FTP Daemon", written from the ground up with security in mind. . It supports both anonymous and non-anonymous FTP access, PAM authentication, bandwidth limiting, and the Linux sendfile() facility. Description-md5: 81386f72ac91a5ea48f8db0b023f3f9b Homepage: https://vsftpd.beasts.org/ Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug Origin: Ubuntu Supported: 5y </[email protected]></[email protected]>
18. Download package with apt
In some cases, you will need to download .deb packages without installing using the apt command. Below command will download apache2 package to the current working directory.
sudo apt download apache2
OR
sudo apt-get download apache2
Note: When you use apt download command, the command will download the package along with its dependencies in a single tar.gz file, whereas, the apt-get download command will only download the single .deb package.
19. Cleanup packages with apt
Performing cleanup activities lets you save the system disk space used by old archived software packages. To clear out the local repository of retrieved software package files, run the below commands.
sudo apt clean
OR
sudo apt-get clean
Note: autoclean removes only the packages that can no longer be downloaded, and are useless. However, it keeps the other packages for future installation.
sudo apt autoclean
OR
sudo apt-get autoclean
20. Edit sources file with apt
With the apt command, you can edit the /etc/apt/sources.list using the text editor. The advantage of using this editor is that it checks for errors after you save and close it.
apt edit-sources
That’s All.
Reference
It’s FOSS – Difference between apt and apt-get.
