How To Install Cockpit on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 & Fedora 28
Cockpit is a free web-based administration tool for the system admin to perform tasks, such as storage management, network configuration, inspecting logs, managing containers, and so on.
Cockpit is released under the LGPL v2.1+, and it is available for Debian, Redhat, CentOS, Fedora, Atomic, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu.
Features
- Manage multiple Cockpit machines from a single Cockpit session
- Create and manage Docker containers
- Create and manage KVM, oVirt Virtual Machines
- Modify the network settings
- Manage user accounts
- Web-based shell in a terminal
- View system performance in a graph.
- Collect system configuration and diagnostic information with the use of sosreport.
Here, we will see how to install Cockpit on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 & Fedora 28 WS.
Install Cockpit
Enable Extras repository on RHEL 7.
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
Install the Cockpit package.
### CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 ### yum install -y cockpit cockpit-networkmanager cockpit-dashboard cockpit-storaged cockpit-packagekit ### Fedora ### sudo dnf install -y cockpit
Additional Packages
You can additionally install below packages to manage other tasks using Cockpit.
| Package Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| cockpit-docker | Managing Docker Containers |
| cockpit-kubernetes | Visualizing and Configuring Kubernetes Cluster |
| cockpit-machines | Manage KVM Virtual Machines |
| cockpit-sosreport | Create diagnostic report with the sosreport tool |
| cockpit-selinux | Troubleshoot SELinux Issues |
| cockpit-kdump | Configure Kernel Crash Dumps |
| cockpit-subscriptions | Manage System subscription |
| cockpit-machines-ovirt | Manage oVirt Virtual Machines |
| cockpit-pcp | Reading PCP metrics and Loading PCP archives |
Enable the Cockpit service.
### CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 ### systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket ### Fedora ### sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Firewall
Add the firewall rules to allow Cockpit to communicate with remote machines as well as to allow us to access Cockpit dashboard from external machines.
### CentOS 7 ### firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=cockpit firewall-cmd --reload ### RHEL 7 ### sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent ### Fedora ### sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent
Working with Cockpit
Once you start the Cockpit service, you access the Cockpit console by going to below URL using the browser.
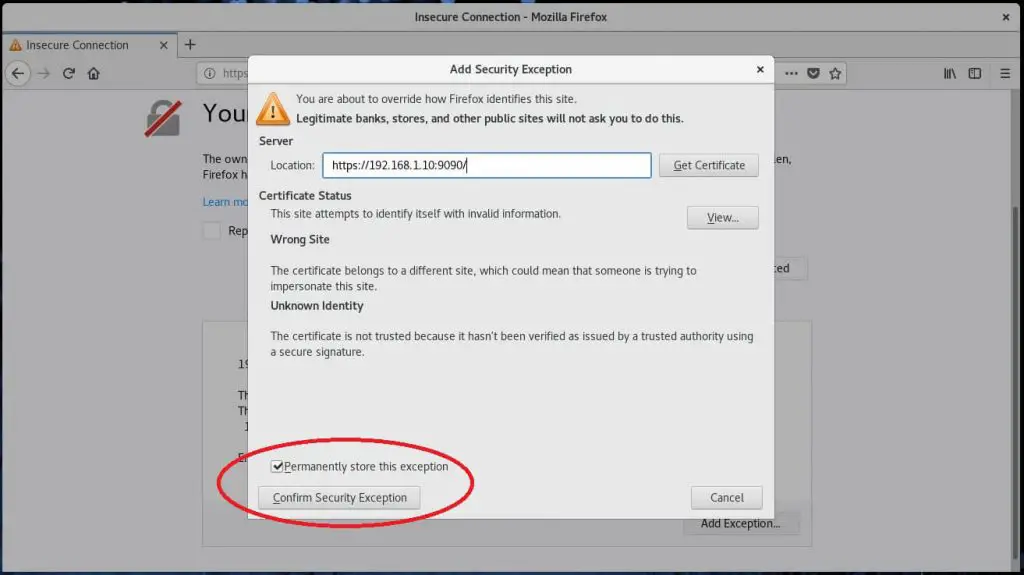
You would need to add a Security Exception in the browser to access the Cockpit for the first time.
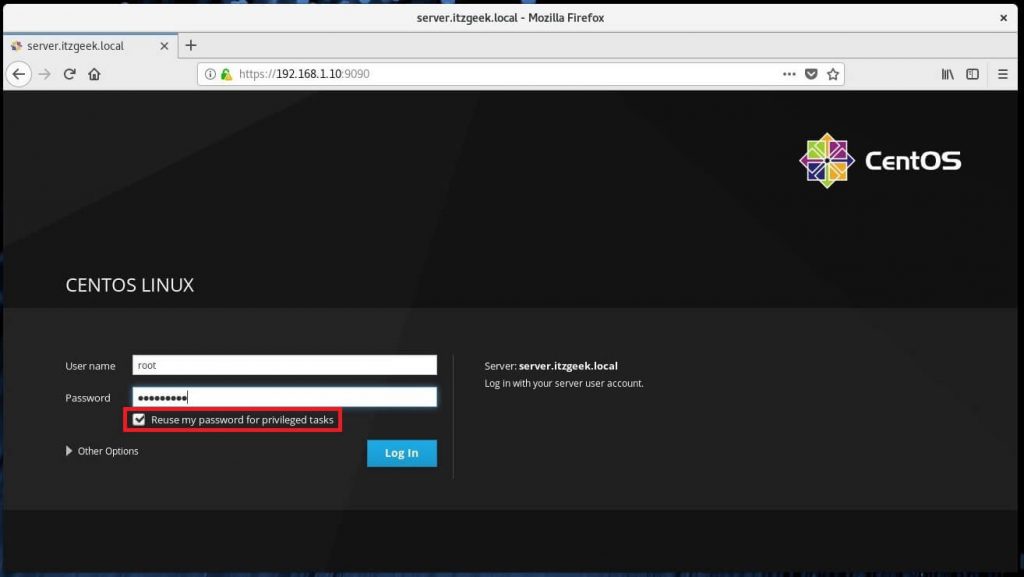
Log in with your local user account. In my case; it is “root”.
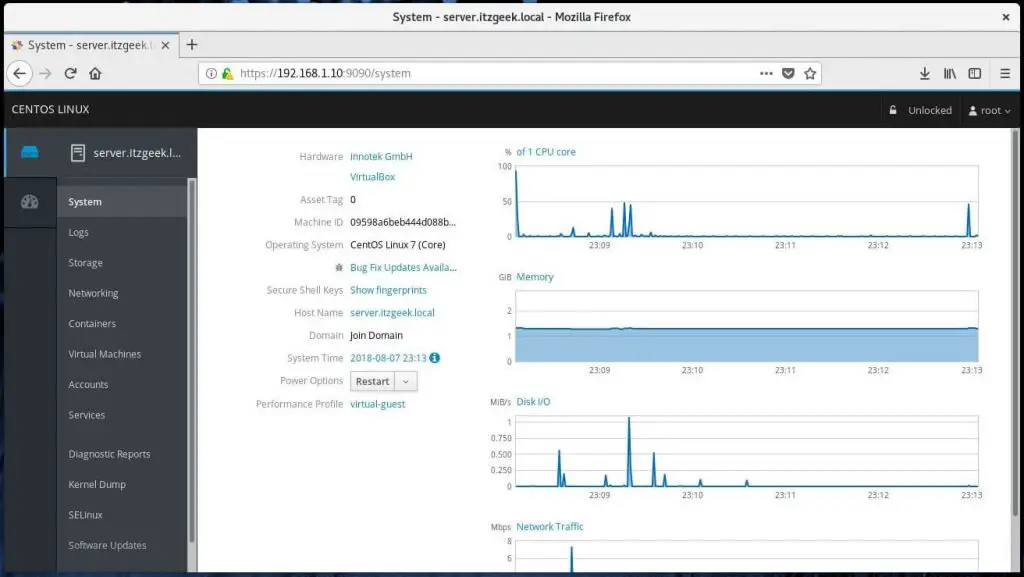
Once you have logged in into Cockpit, it will take you to the System page where you can see a complete overview of the system.
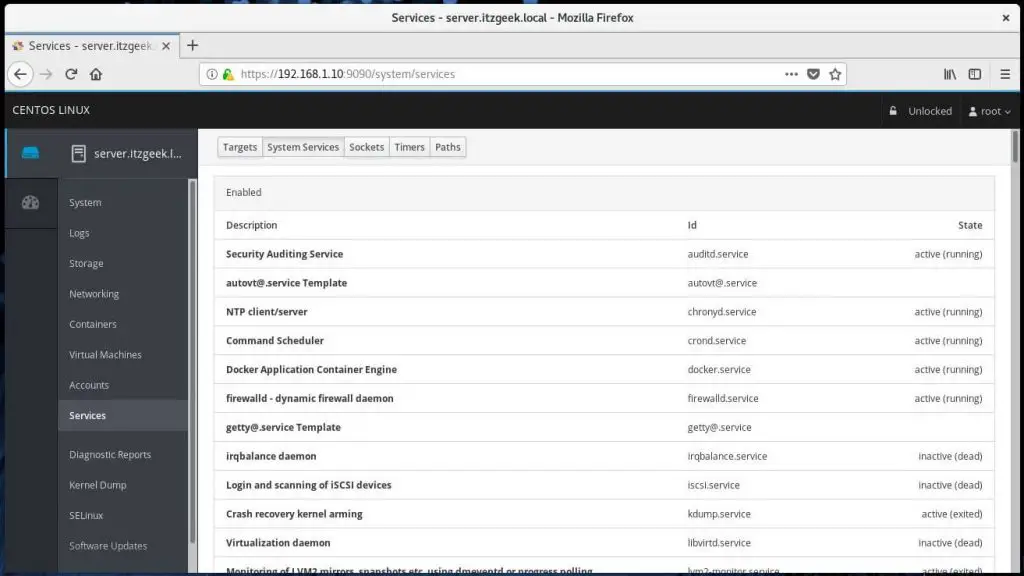
You can see the details of running services by clicking on Services. Here, you can manage (start, stop, restart, etc.) the services by clicking on a particular service.
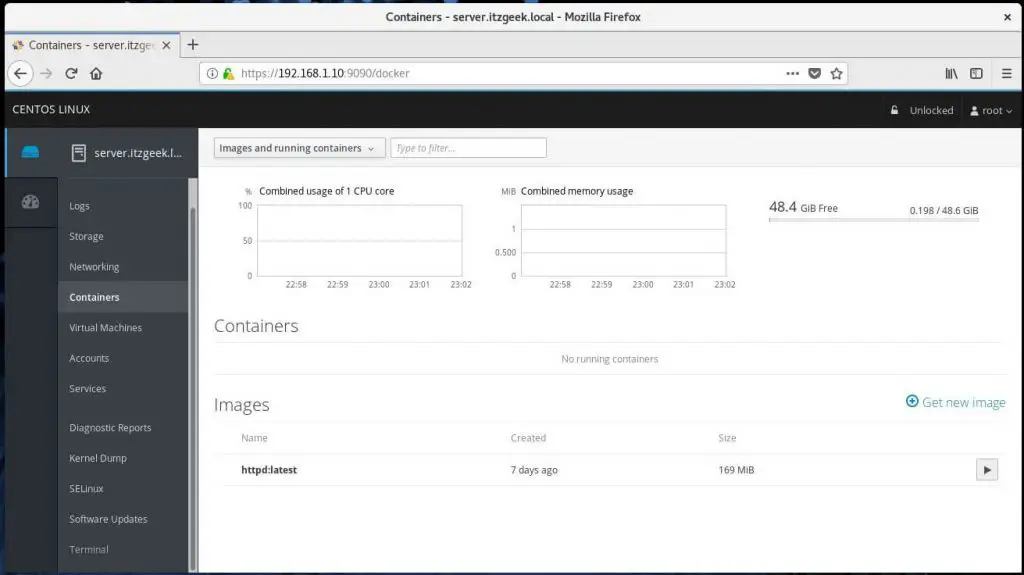
If you would like to manage the Docker containers, you have to go to Containers page. Here, you can run, stop, delete and commit a container.
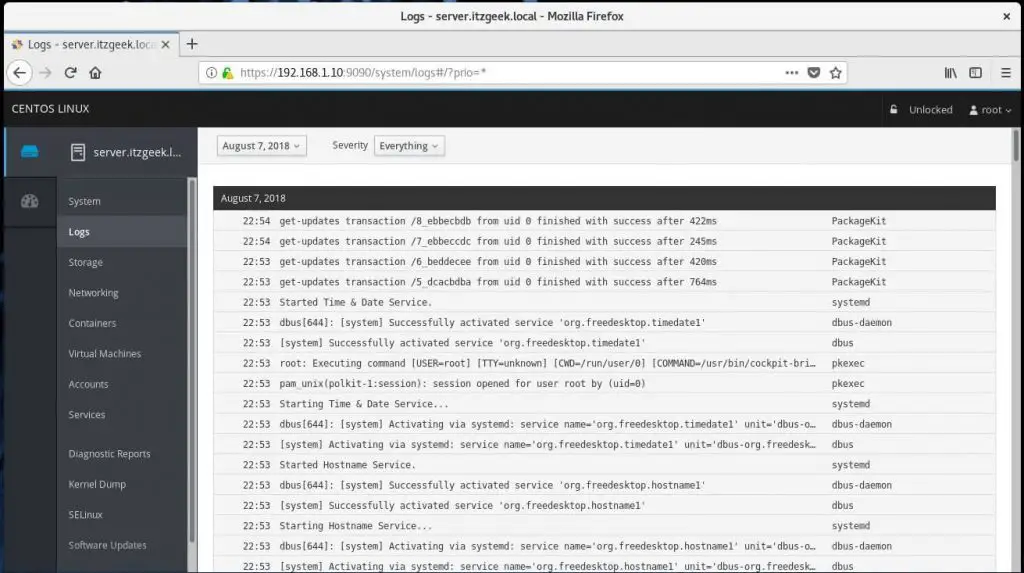
You can troubleshoot your machine by having a look at Logs.
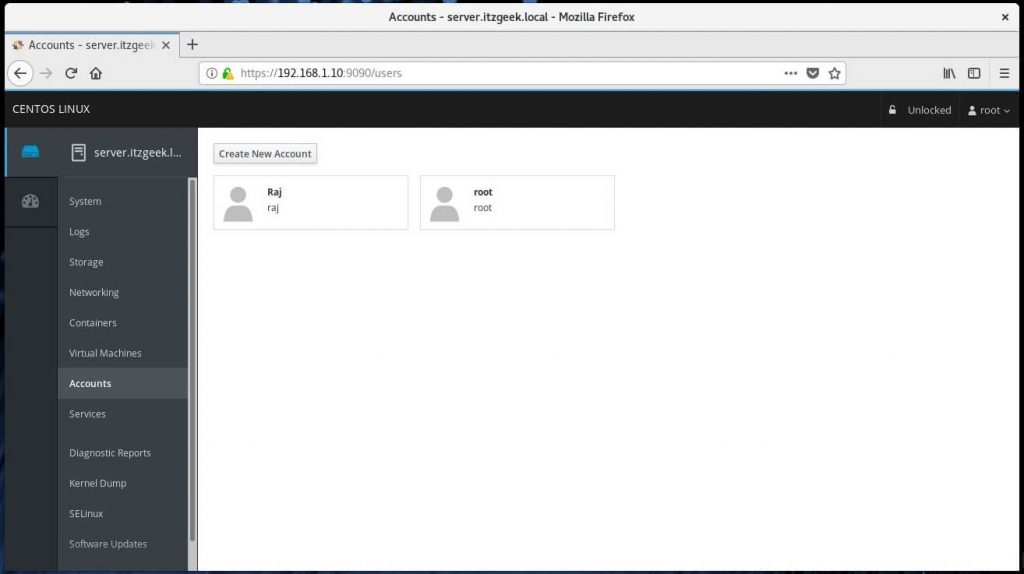
Manage the system users by going to Accounts.
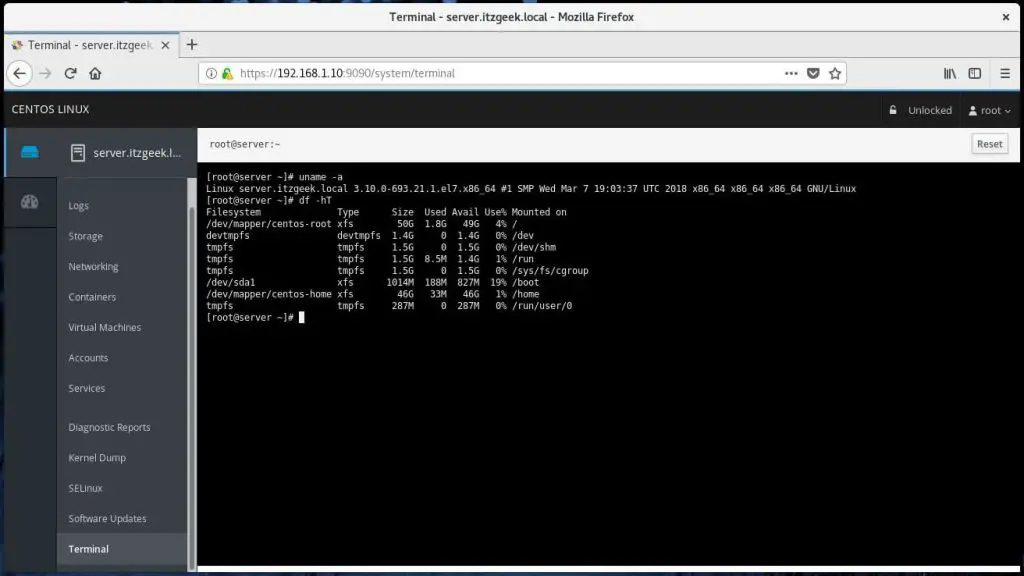
You can also take the terminal of the server by clicking on the Terminal.
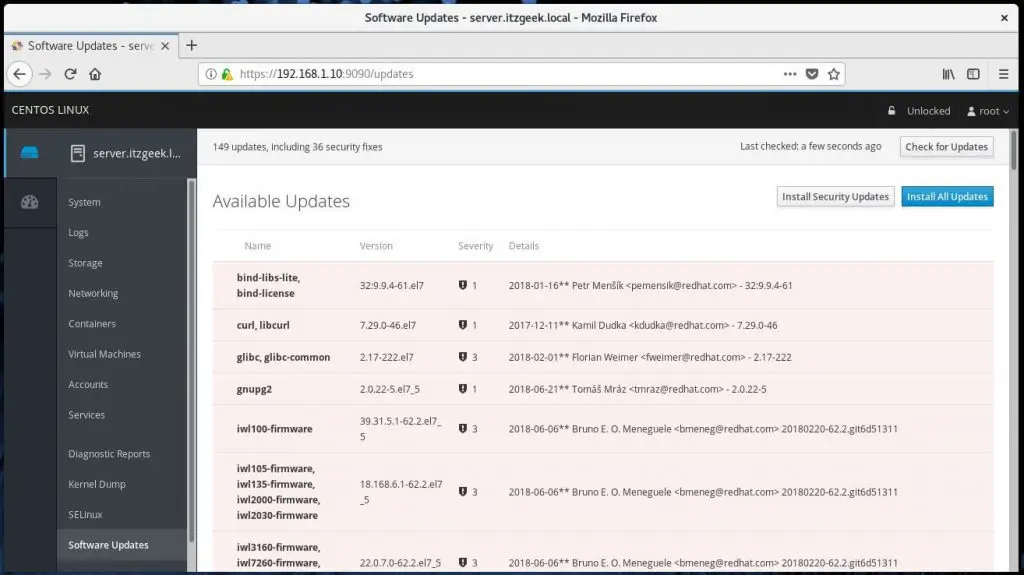
You can seamlessly update the system packages using Software Updates.
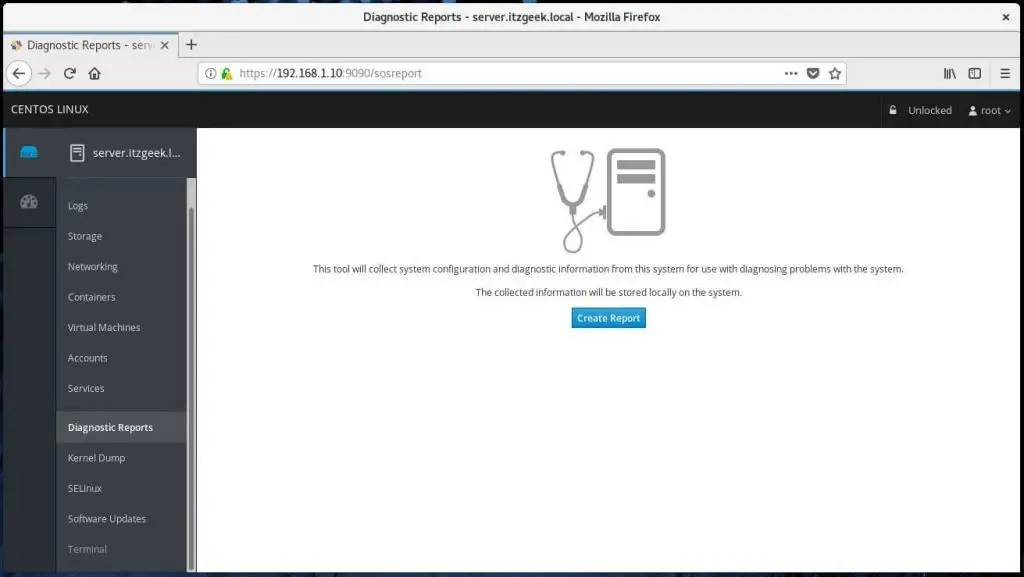
Generate sosreport and share with support team by going to Diagnostic Reports using Cockpit.
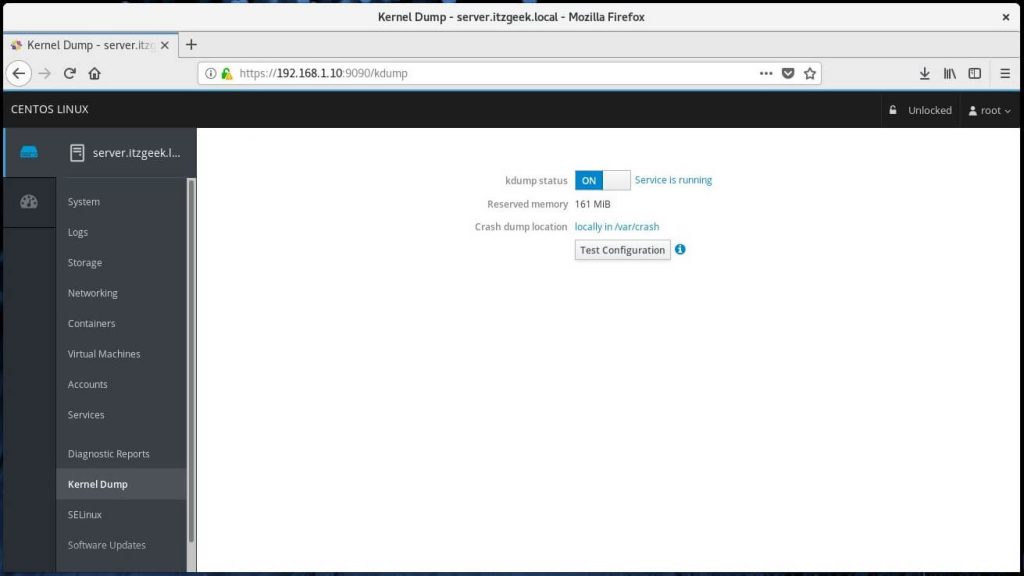
Manage kernel crash dump by going to Kernel Dump.
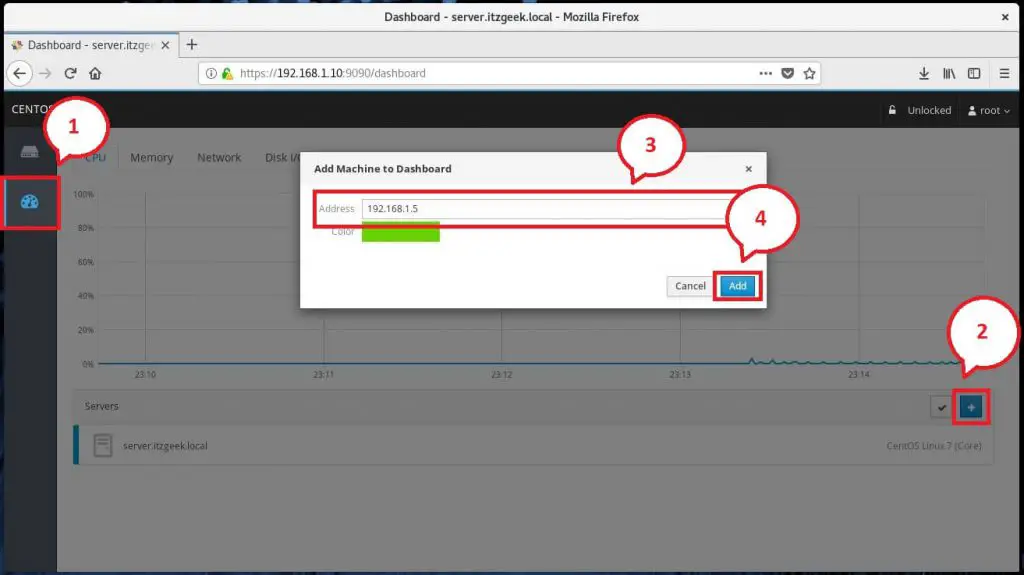
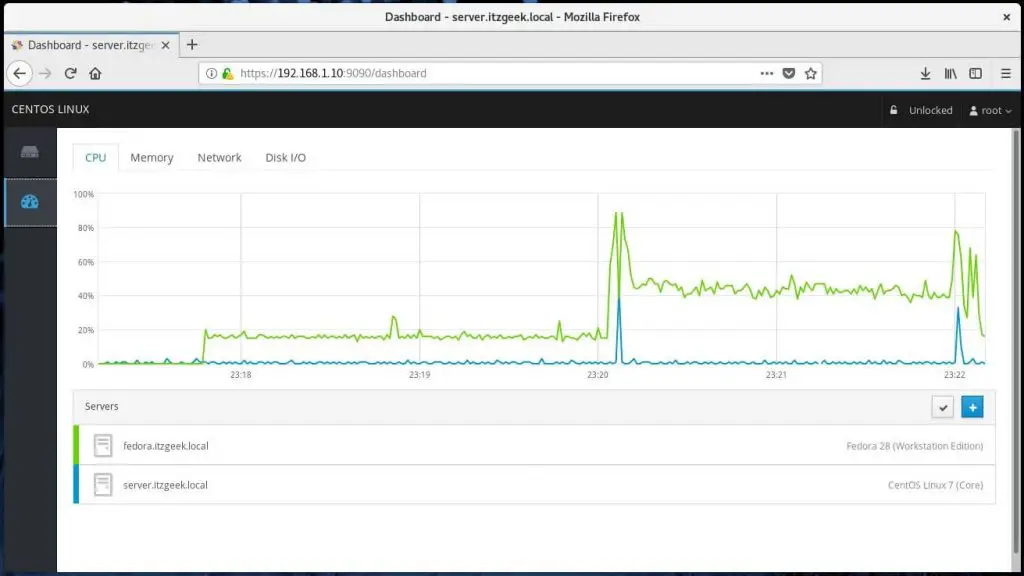
Manage Multiple Servers with Cockpit
To manage multiple servers with Cockpit, click on Dashboard and then click on Plus sign icon and add them one by one.
List of machines connected to Cockpit:
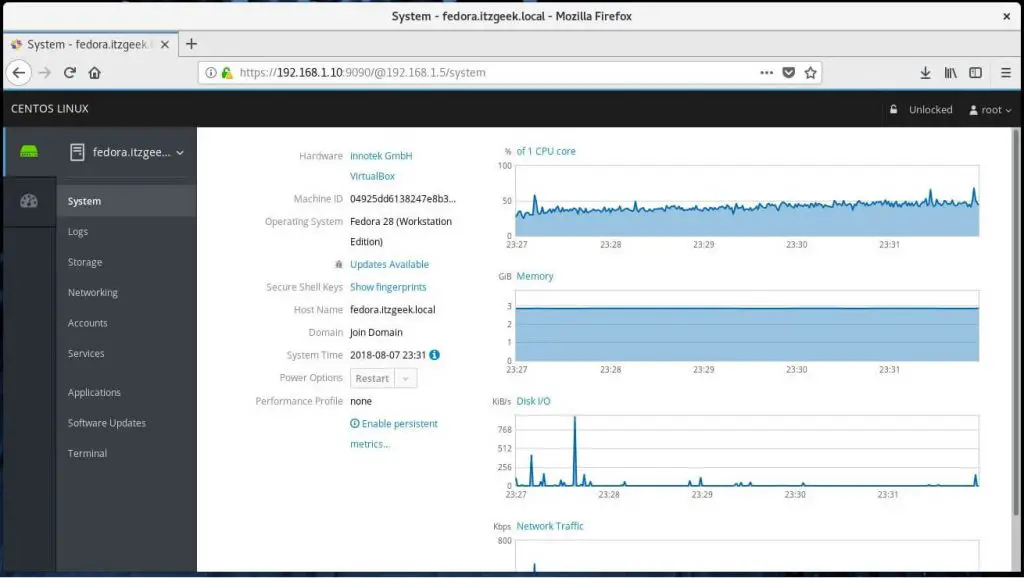
Overview of the remote system:
That’s All.
