How To Install Katello 3.10 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
Katello is an open source lifecycle management plugin for Foreman which helps you handle the subscription, and repository management. Katello connects to external repositories for the content (updates) and downloads it; you can apply them (update) to the subscribed systems.
You can also say that Katello is the alternate to Redhat Satellite or SpaceWalk.
Katello also allows you to perform tasks such as machine provisioning, configuration management using foreman.
Components of Katello
Inner Components
Candlepin – It handles subscription management.
Pulp – handles repository and content management.
Smart Proxy – It acts as a proxy for some of the services like DNS, DHCP, and Puppetmaster configuration.
Outer Components
Foreman – An open source application that allows you to provision physical and virtual systems automatically using Kickstart and Puppet modules.
In this post, we are going to install Katello (v3.10) on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
Hardware Requirments
- 2 CPU
- 8GB RAM (12GB RAM recommended)
- 20GB for / filesystem.
- Supports only CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
- /var/lib/pulb holds the operating systems repository content, so allocate 30GB of space for each operating system you wish to sync.
Prerequisites
Use the following command to set the hostname.
hostnamectl set-hostname katello.itzgeek.local
If you don’t have DNS in your environment, then update the /etc/hosts file.
echo "192.168.1.10 katello.itzgeek.local itzgeek" >> /etc/hosts
Upgrade your base operating system to the latest version (Recommended).
READ: How to Update CentOS 7.0 / 7.1 / 7.2 / 7.3 / 7.4 to CentOS 7.5
Set the firewall rules for Katello.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp --add-port=443/tcp --add-port=5647/tcp --add-port=9090/tcp
Additionally for the smart proxy.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8140/tcp --add-port=8443/tcp --add-port=8000/tcp --add-port=67/udp --add-port=68/udp --add-port=69/udp
Reload the firewall.
firewall-cmd --reload
Configure NTP service so that your server can sync time with upstream time server for accurate timing.
yum install -y ntp
service ntpd restart
# Set timezone if required
timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York
ntpdate -u us.pool.ntp.org
You may need to enable following repositories only on RHEL 7.
### RHEL 7 Only ###
yum install -y yum-utils
yum-config-manager --disable "*"
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-7-server-rpms
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-7-server-optional-rpms
yum-config-manager --enable rhel-7-server-extras-rpms
Configure required repositories for Katello.
yum -y localinstall https://fedorapeople.org/groups/katello/releases/yum/3.10/katello/el7/x86_64/katello-repos-latest.rpm yum -y localinstall https://yum.theforeman.org/releases/1.20/el7/x86_64/foreman-release.rpm yum -y localinstall https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppetlabs-release-pc1-el-7.noarch.rpm yum -y localinstall https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm yum -y install foreman-release-scl python2-django
Run the following command to install Katello packages.
yum -y install katello
Use foreman-installer to setup Katello.
foreman-installer --scenario katello
Upon completion of Katello setup, foreman-installer will display the account details (blue). You would need this information to log in into Foreman dashboard.
Resetting puppet server version param... Installing Done [100%] [..................................................] Success! * Katello is running at https://katello.itzgeek.local Initial credentials are admin / 9aHprevR8atx4cuV * To install an additional Foreman proxy on separate machine continue by running: foreman-proxy-certs-generate --foreman-proxy-fqdn "$FOREMAN_PROXY" --certs-tar "/root/$FOREMAN_PROXY-certs.tar" The full log is at /var/log/foreman-installer/katello.log
Access Katello
Now, open up your web browser and navigate to the following URL.
OR
Log in into Katello using the credentials you got during the setup.
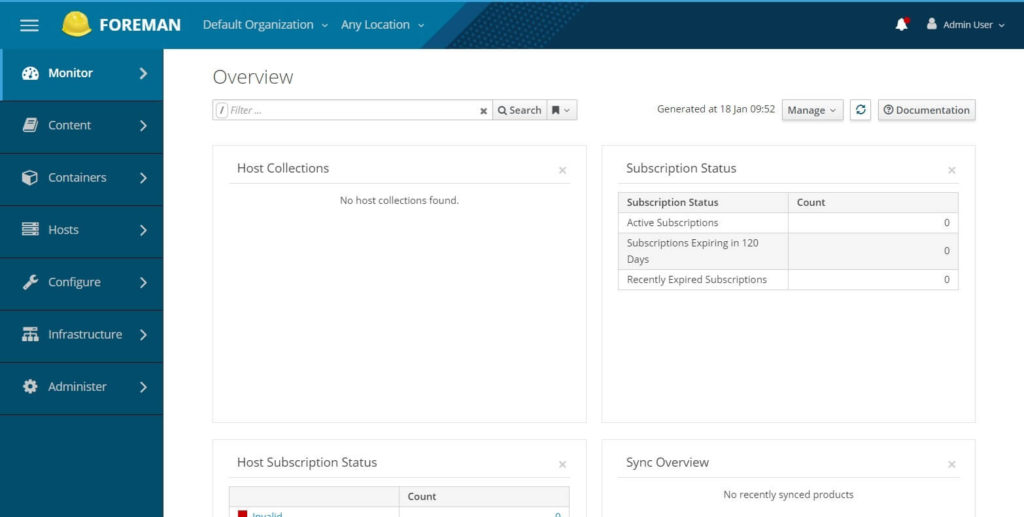
The homepage of Katello / Foreman will look like below.
If you wish to change the password of admin user, go to Admin User >> My Account.
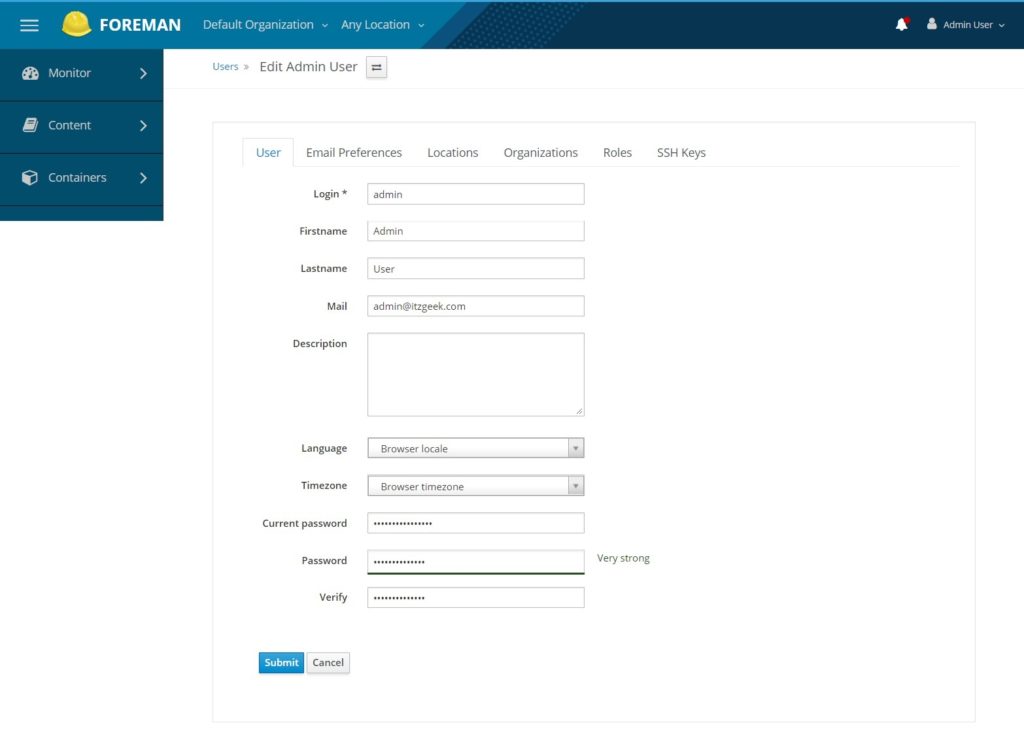
Change the password.
In our next article, we will be Configuring Katello to deliver patches for CentOS / RHEL clients.
That’s All
