How To Install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11 / Debian 10
phpMyAdmin is a free and open-source, web-based tool for managing the MySQL and MariaDB servers. It is widely used to manage the database by web hosting companies and administrators who are new to the database.
phpMyAdmin helps the system administrator to perform databases activities such as creating, deleting, querying, database, tables, columns, etc.
In this post, we will see how to install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11 / Debian 10.
Prerequisites
Install MariaDB / MySQL Server
To install phpMyAdmin, your system must have a database instance running and an Nginx web server.
Standalone Database
Follow the below tutorials and prepare your system for setting up phpMyAdmin.
Step 1: How To Install MariaDB on Debian 10 / How To Install MariaDB on Debian 11 / How To Install MySQL 8.0/5.7 on Debian 11/10
Then,
Step 2: How To Install LEMP Stack on Debian 10 / How To Install LEMP Stack on Debian 11
Install PHP extensions for phpMyAdmin to connect with the database.
sudo apt install -y php-json php-mbstring php-xml
LEMP Stack
READ: How To Install LEMP Stack on Debian 10 / How To Install LEMP Stack on Debian 11
Install PHP extensions for phpMyAdmin to connect with the database.
sudo apt install -y php-json php-mbstring php-xml
Install phpMyAdmin
The phpMyAdmin package is now available in the Debian repository. But, we do not use it here since it is an older version. So, we will download the latest version from the official website.
wget https://files.phpmyadmin.net/phpMyAdmin/5.1.1/phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages.tar.gz
Extract phpMyAdmin using the tar command.
tar -zxvf phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages.tar.gz
Move the phpMyAdmin to your desired location.
sudo mv phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Configure phpMyAdmin
Copy the sample configuration file.
sudo cp -pr /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.sample.inc.php /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
Edit the configuration file.
sudo nano /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
Generate a blowfish secret and update the secret in the configuration file.
$cfg['blowfish_secret'] = 'CfX1la/aG83gx1{7rADus,iqz8RzeV8x'; /* YOU MUST FILL IN THIS FOR COOKIE AUTH! */
Also, uncomment the phpMyAdmin storage settings.
/** * phpMyAdmin configuration storage settings. */ /* User used to manipulate with storage */ $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlhost'] = 'localhost'; // $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlport'] = ''; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controluser'] = 'pma'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlpass'] = 'pmapass'; /* Storage database and tables */ $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pmadb'] = 'phpmyadmin'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['bookmarktable'] = 'pma__bookmark'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['relation'] = 'pma__relation'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_info'] = 'pma__table_info'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_coords'] = 'pma__table_coords'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pdf_pages'] = 'pma__pdf_pages'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['column_info'] = 'pma__column_info'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['history'] = 'pma__history'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_uiprefs'] = 'pma__table_uiprefs'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['tracking'] = 'pma__tracking'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['userconfig'] = 'pma__userconfig'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['recent'] = 'pma__recent'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['favorite'] = 'pma__favorite'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['users'] = 'pma__users'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['usergroups'] = 'pma__usergroups'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['navigationhiding'] = 'pma__navigationhiding'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['savedsearches'] = 'pma__savedsearches'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['central_columns'] = 'pma__central_columns'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['designer_settings'] = 'pma__designer_settings'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['export_templates'] = 'pma__export_templates';
Credit: TECHIES WORLD
Import the create_tables.sql to create tables for phpMyAdmin.
sudo mysql < /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/sql/create_tables.sql -u root -p
Login to MariaDB.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Add the user and grant permission to phpMyAdmin’s database.
CREATE USER 'pma'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'pmapass'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON phpmyadmin.* TO 'pma'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Create a virtual host configuration file for phpMyAdmin (Ex. phpMyAdmin.conf) under the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
Use the following information to create a virtual host for phpMyAdmin. Change the domain name (server_name) as per your requirement.
server {
listen 80;
server_name pma.itzgeek.local;
root /usr/share/phpMyAdmin;
location / {
index index.php;
}
## Images and static content is treated different
location ~* ^.+.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|xml)$ {
access_log off;
expires 30d;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
location ~ /(libraries|setup/frames|setup/libs) {
deny all;
return 404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/share/phpMyAdmin$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}
Create a tmp directory for phpMyAdmin and then change the permission.
sudo mkdir /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/tmp sudo chmod 777 /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/tmp
Set the ownership of the phpMyAdmin directory.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Restart the services.
sudo systemctl restart nginx sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Create DB & User
By default, the MariaDB root user is allowed to log in locally via Unix socket (MariaDB v10.4 and below). So, we will create a database user and login to phpMyAdmin with that user.
CREATE DATABASE app_db; CREATE USER 'app_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON app_db.* TO 'app_user'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
If required, you can disable Unix socket authentication and enable native password login.
Access phpMyAdmin
Access the phpMyAdmin using the browser by going to the below URL.
Log in with the database user we just created in the previous step.
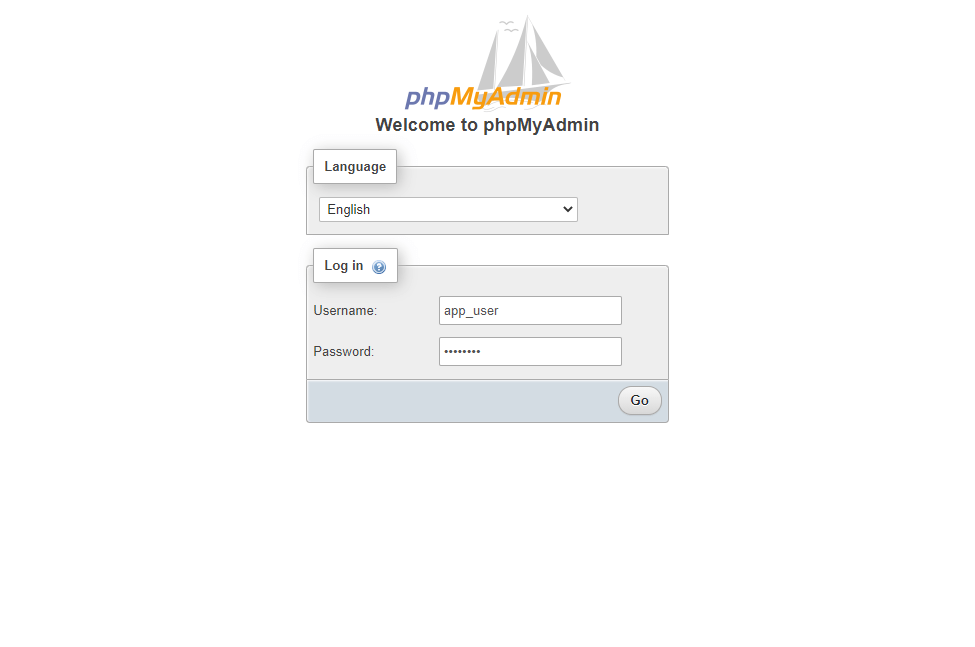
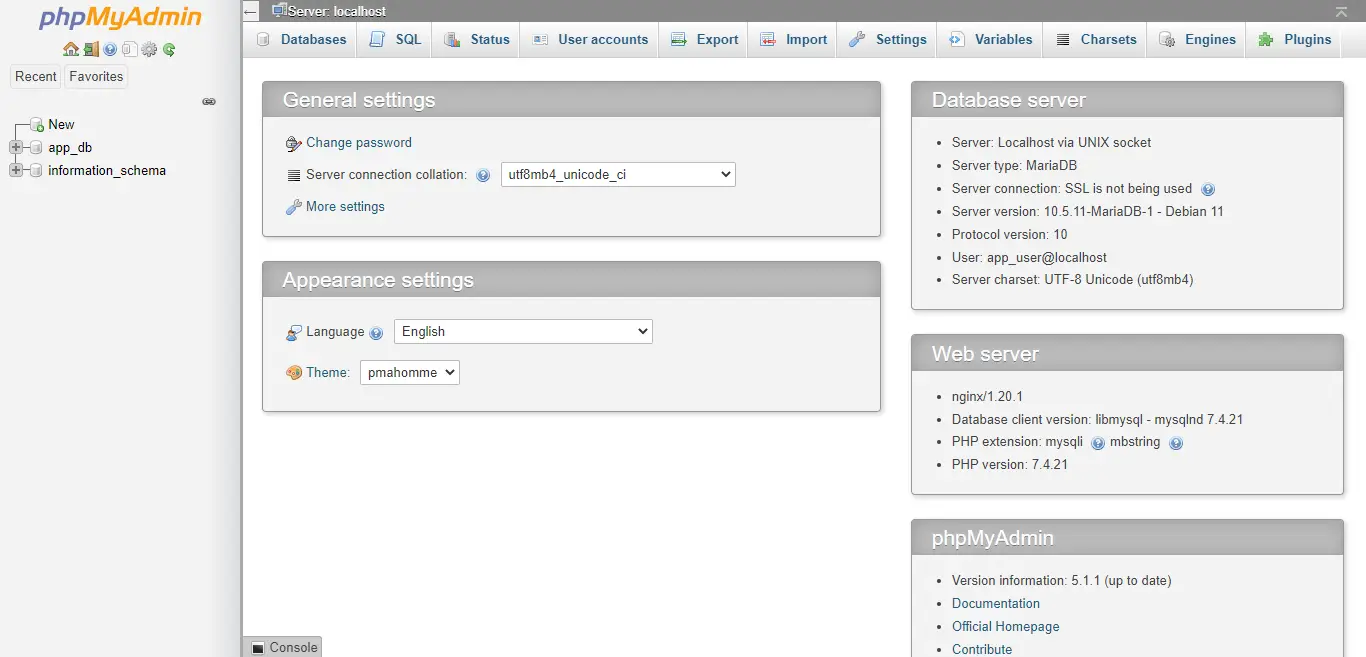
You will get the home page where you can manage databases.
Conclusion
I hope this post helped you install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11 / Debian 10. Please share your feedback in the comments section.
