Subversion, also known as SVN, an open-source version control system. It is used to keep track of source file and documents.
Any time you change, add or delete a file or folder that you control with Subversion, you commit these changes to the Subversion repository, which creates a new revision in the repository reflecting these changes.
Whenever you required, you can always go back, look at and get the contents of previous revisions.
This post helps you setup SVN on Debian 9 / Ubuntu 16.04.
Switch to the root user.
su -
OR
sudo su -
Install web server
let us first update the repository index.
apt-get update
Here, we will install Apache server for accessing SVN server using HTTP URLs.
apt-get install -y apache2 apache2-utils
Allow Apache through the firewall (If applicable).
ufw allow 80/tcp ufw reload
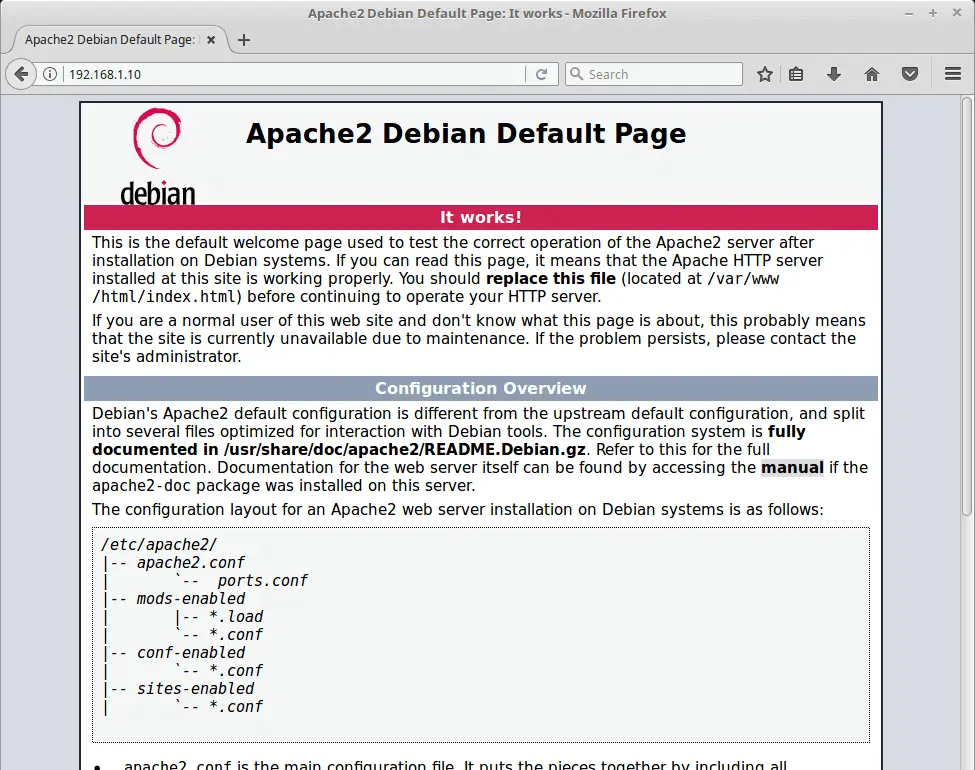
Verify the Apache service by visiting below URL.
You should get Apache2 default page.
Install Subversion
Once the Apache is installed, you can issue the following command to install the Apache subversion.
### debian ### apt-get install -y subversion subversion-tools libapache2-mod-svn ### ubuntu ### apt-get install -y subversion subversion-tools libapache2-mod-svn libapache2-svn
Configure Subversion
Once the installation is done, create a repository as per your requirements. Here, I am creating /var/lib/svn as the base and will create a “testrepo” repository in it.
mkdir /var/lib/svn
Create the repository called “testrepo”
svnadmin create /var/lib/svn/testrepo
Change the permission of the repository to let Apache read and write data onto it.
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/lib/svn/testrepo/
Configure virtual host in Apache.
nano /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/dav_svn.conf
Place the following content.
<Location /svn> DAV svn SVNParentPath /var/lib/svn AuthType Basic AuthName "Subversion Repository" AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd Require valid-user </Location>
Create a password file for the user. Replace raj with your username.
htpasswd -cm /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd raj
Restart the apache server.
systemctl restart apache2
Test Subversion
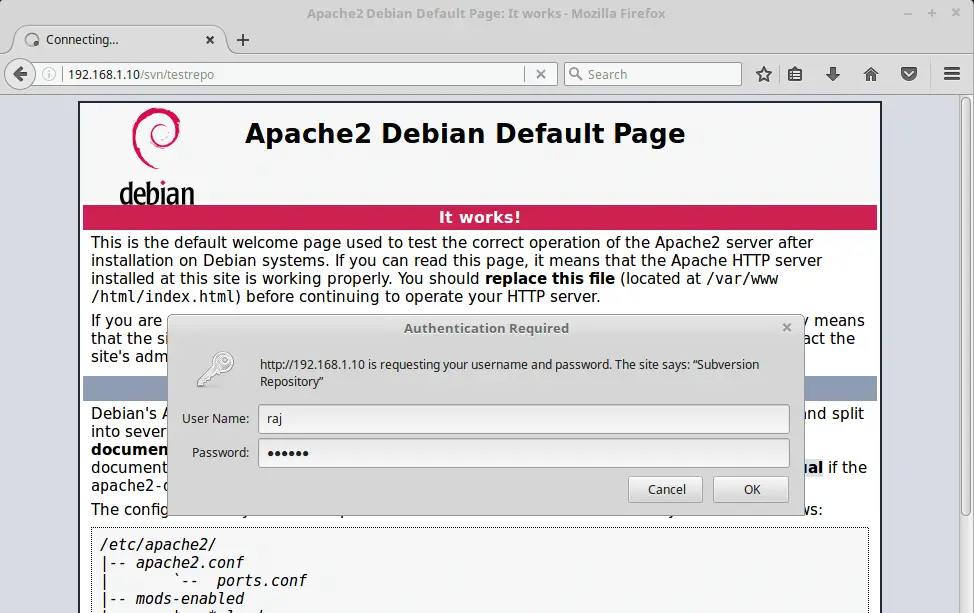
Access the SVN using a browser, URL will be
You will be asked to enter the username and password.
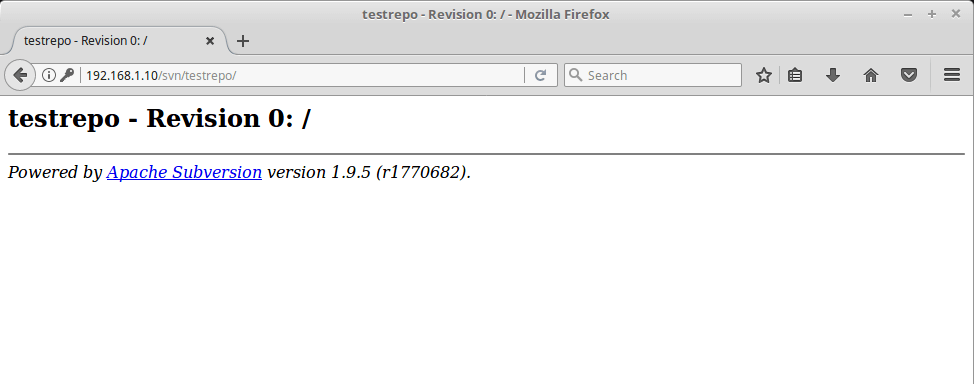
Upon successful login, the content will be listed like below.
Create a directory called “checkout”
mkdir checkout
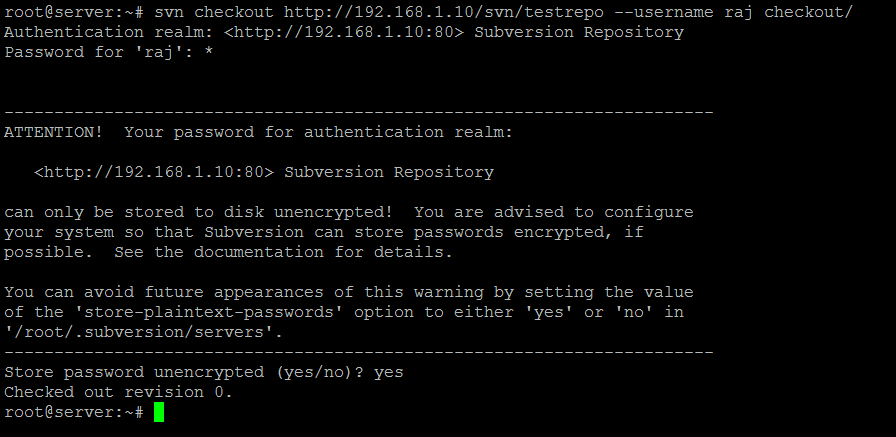
Check out the files contained within the repository to the testing directory. Replace raj with your username.
svn checkout https://192.168.1.10/svn/testrepo --username raj checkout/
The output will be like below.
Authentication realm: <https://192.168.1.10:80> Subversion Repository Password for 'raj': **** <-- Enter Password ----------------------------------------------------------------------- ATTENTION! Your password for authentication realm: <https://192.168.1.10:80> Subversion Repository can only be stored to disk unencrypted! You are advised to configure your system so that Subversion can store passwords encrypted, if possible. See the documentation for details. You can avoid future appearances of this warning by setting the value of the 'store-plaintext-passwords' option to either 'yes' or 'no' in '/root/.subversion/servers'. ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Store password unencrypted (yes/no)? yes <-- Store Password Checked out revision 0.
Create test files for committing on the testrepo repository.
cd checkout/ touch checkout1.txt touch checkout2.txt
Add those created files for committing.
svn add checkout1.txt checkout2.txt
Output:
A checkout1.txt A checkout2.txt
Commit the added files. You can mention the commit message with a flag -m.
svn commit -m 'First Revision'
Output:
Adding checkout1.txt Adding checkout2.txt Transmitting file data .. Committed revision 1.
You can view the committed files in a browser.
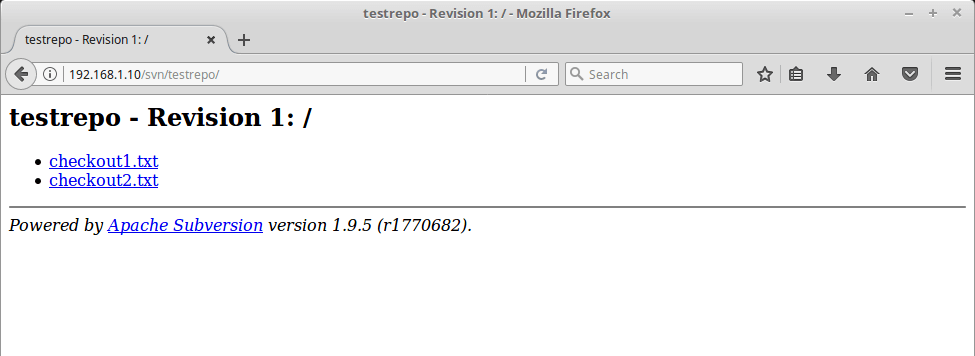
That’s All. You can use SVN clients like TortoiseSVN for windows and Rapidsvn for Linux.
