How To Install Apache Tomcat on Debian 10 / Debian 9
Apache Tomcat is an open-source webserver to run Java web applications developed by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).
Tomcat contains Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages (JSP), Java EL, and WebSocket technologies, and provides a “pure Java” HTTP web server environment for running Java codes.
Here, we will see how to install Apache Tomcat on Debian 10 / Debian 9.
Requirement
Tomcat requires Java JDK 8 or above to be installed on the machine. You can either install Oracle JDK or OpenJDK.
READ: How to Install Oracle JDK on Debian 10 / Debian 9
For this demo, I am going to use OpenJDK.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y default-jdk
Once Java is installed, you can verify the Java version by using the following command.
java -version
Output: openjdk version "11.0.6" 2020-01-14 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.6+10-post-Debian-1deb10u1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.6+10-post-Debian-1deb10u1, mixed mode, sharing)
Install Apache Tomcat
Tomcat Service Account
For best practice, Tomcat should never be run as a privileged user (root). So, create a low-privilege user tomcat for running the Tomcat service.
sudo groupadd tomcat
sudo useradd -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/nologin tomcat
Download Apache Tomcat
Download the latest version of the Apache Tomcat from the official website.
Apache Tomcat 9.x
wget https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.34/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.34.tar.gz
Apache Tomcat 8.x
wget https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.54/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.54.tar.gz
Create a directory for Tomcat.
sudo mkdir /opt/tomcat
Extract the Tomcat tar package and move it /opt/tomcat directory.
tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-*.tar.gz
sudo mv apache-tomcat-*/* /opt/tomcat/
Change the ownership of the directory to tomcat user so that application can write files to it.
sudo chown -R tomcat:tomcat /opt/tomcat/
Start Apache Tomcat
We will configure the systemd to start the Tomcat service. Create a tomcat systemd service file.
Green ones depend on the environment, so change them accordingly.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the below information to Tomcat systemd service file.
Example output: /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java.
[Unit] Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container Wants=network.target After=network.target [Service] Type=forking Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/ Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat Environment='CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1G -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true' Environment='JAVA_OPTS=-Djava.awt.headless=true' ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh SuccessExitStatus=143 User=tomcat Group=tomcat UMask=0007 RestartSec=10 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload systemd daemon.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Start and enable Apache Tomcat service.
sudo systemctl start tomcat
sudo systemctl enable tomcat
By default, Tomcat runs on port 8080. Use can use the netstat command to check the port status.
sudo netstat -antup | grep 8080
Output: tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3834/java
READ: netstat command not found – Quick Fix
Configure Apache Tomcat Web UI
Tomcat comes with the Web Manager and Host Manager for managing the Tomcat server. Both the Host Manager and Web Manager are password-protected.
Only the user with the manager-gui and admin-gui role is allowed to access web manager and host-manager respectively. Those two roles are defined in the tomcat-users.xml file.
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Place the following two lines (role and user definition) just above the last line.
rolename="admin-gui,manager-gui"/>
<user username="admin" password="password" roles="manager-gui,admin-gui"/>
For security reasons, the Web Manager and Host Manager is accessible only from the localhost, i.e., from the server itself.
To access managers from the remote system, you need to add your source network to the allow list.
To do that, edit the below two files.
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml sudo nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
Update the below line on both files with source IP from which you are accessing the Web and Host Manager. .* will allow everyone to have access to managers.
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1|.*" />
OR
You can allow only part of your network. For example, to allow only the 192.168.0.0/24 network, you can use the below values.
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 |192.168.0.*" />
Restart the Tomcat service.
sudo systemctl restart tomcat
Access Apache Tomcat
Open the web browser and point it to,
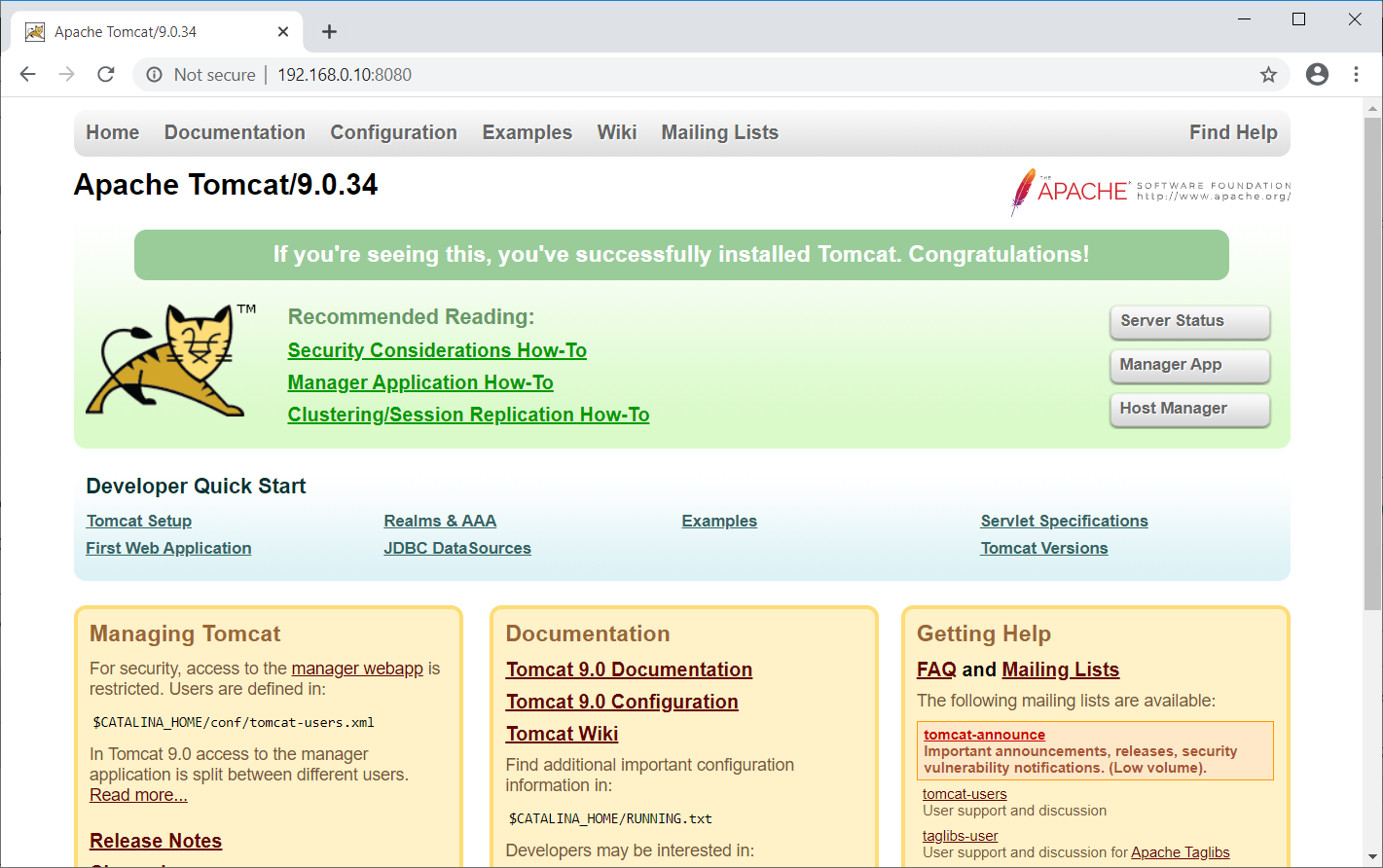
You would get the Tomcat default page, and this page confirms the successful installation of Tomcat.
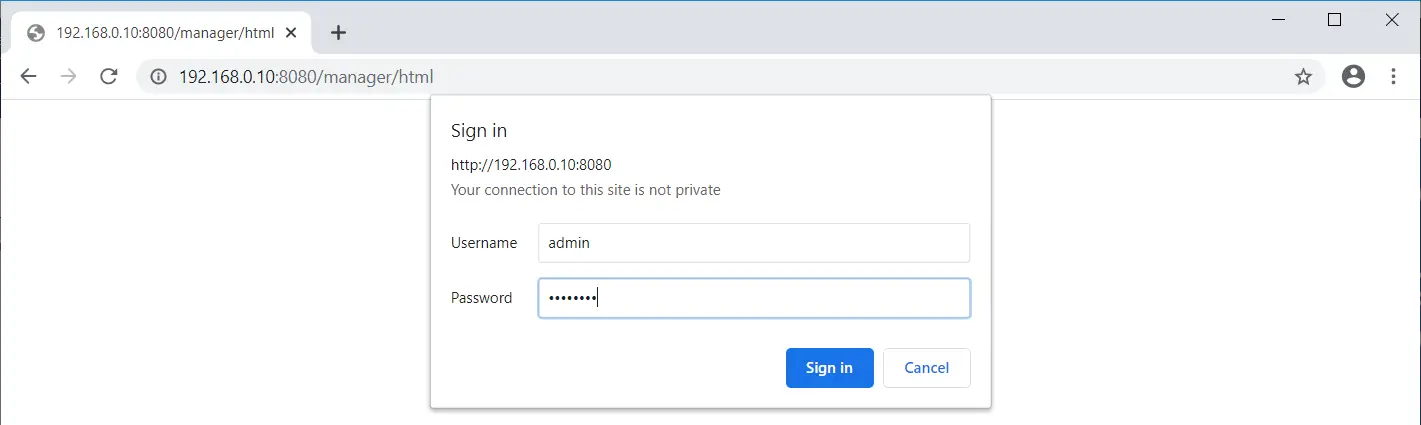
Click Manager App to access web application manager: Login Required. Username: admin, Password: password.
Here, you can deploy a new application, deploy an application on a specified context, start, stop, reload, and un-deploy an application.
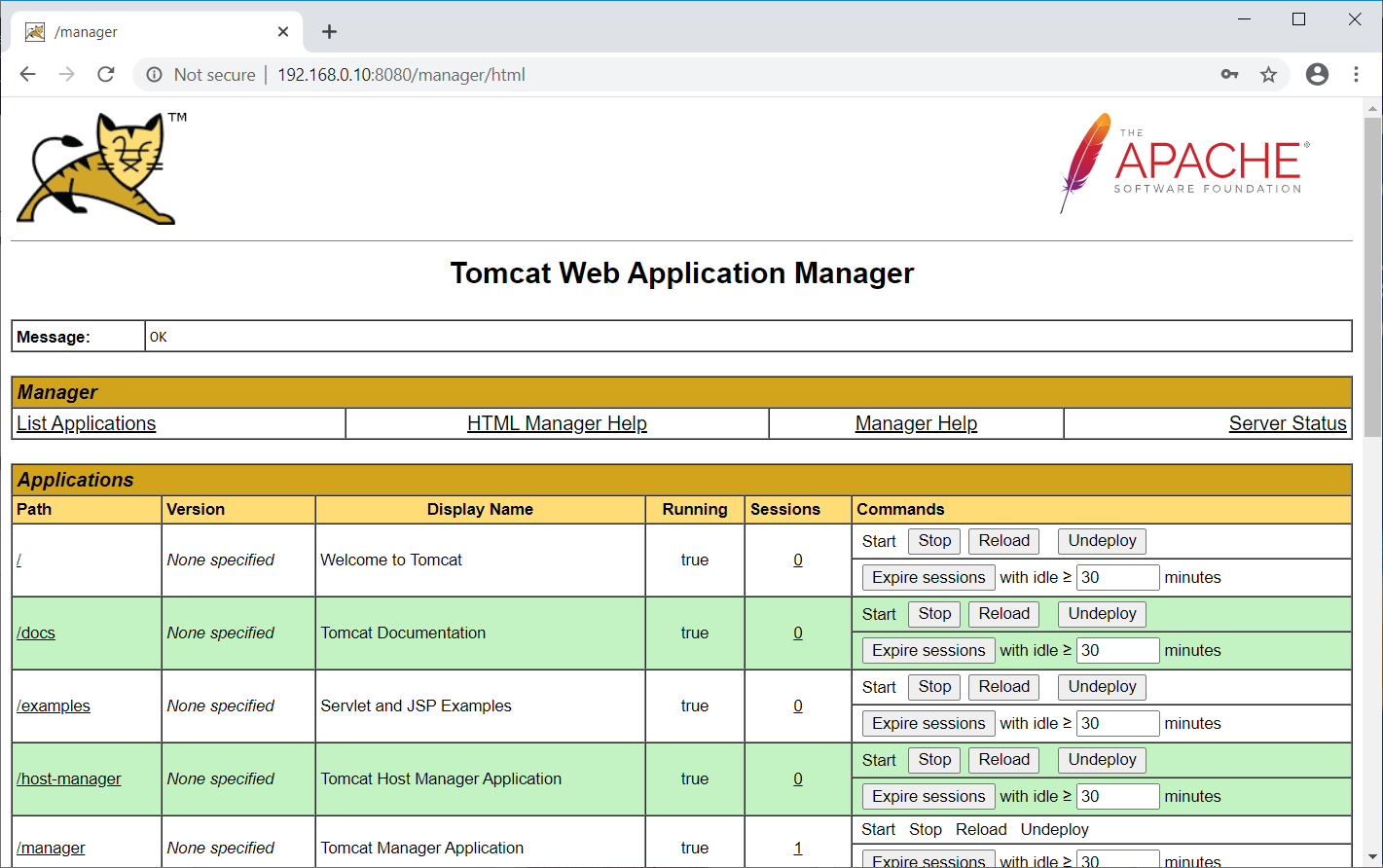
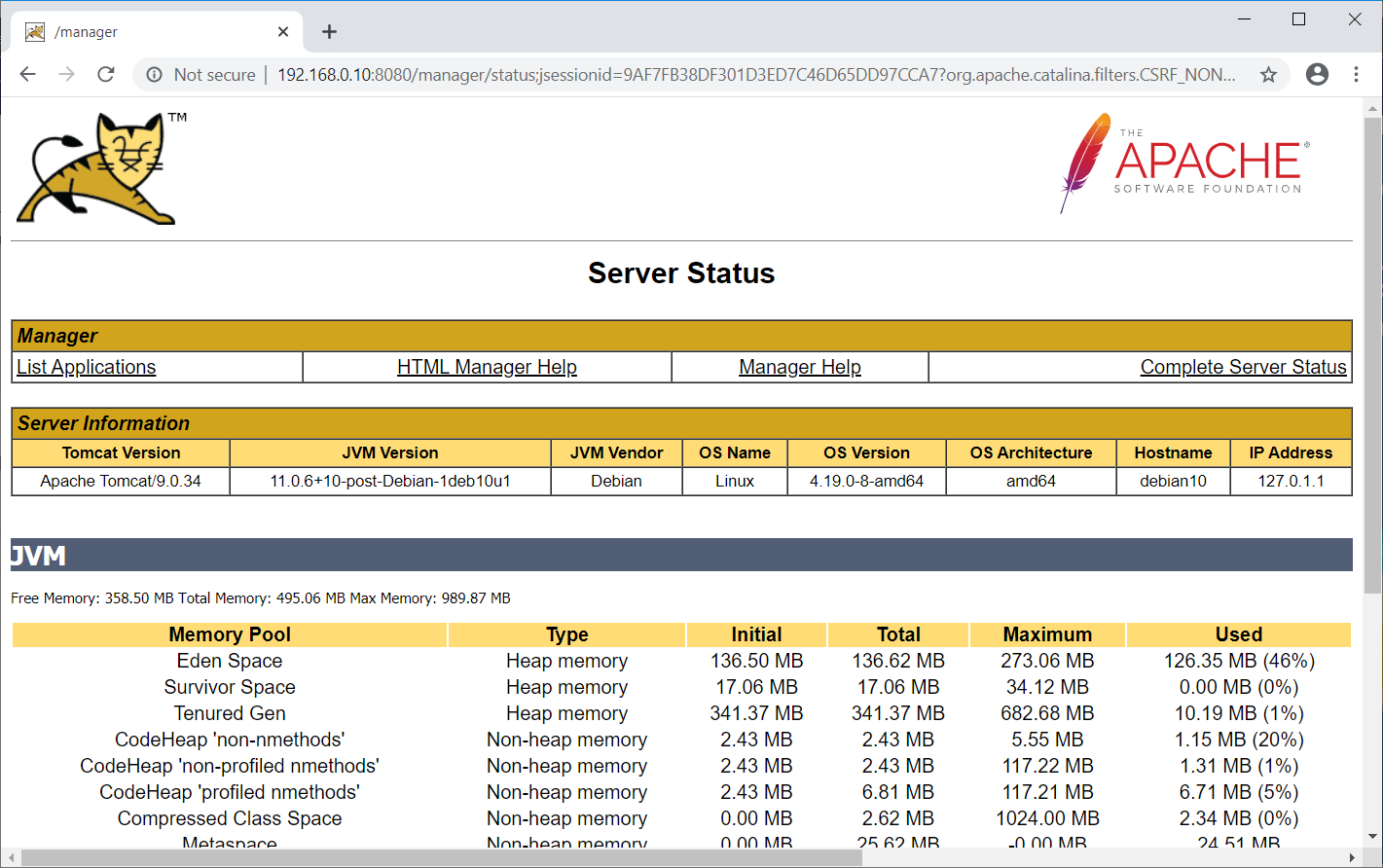
Also, you can check the server status clicking on Server Status on the above page (web application manager).
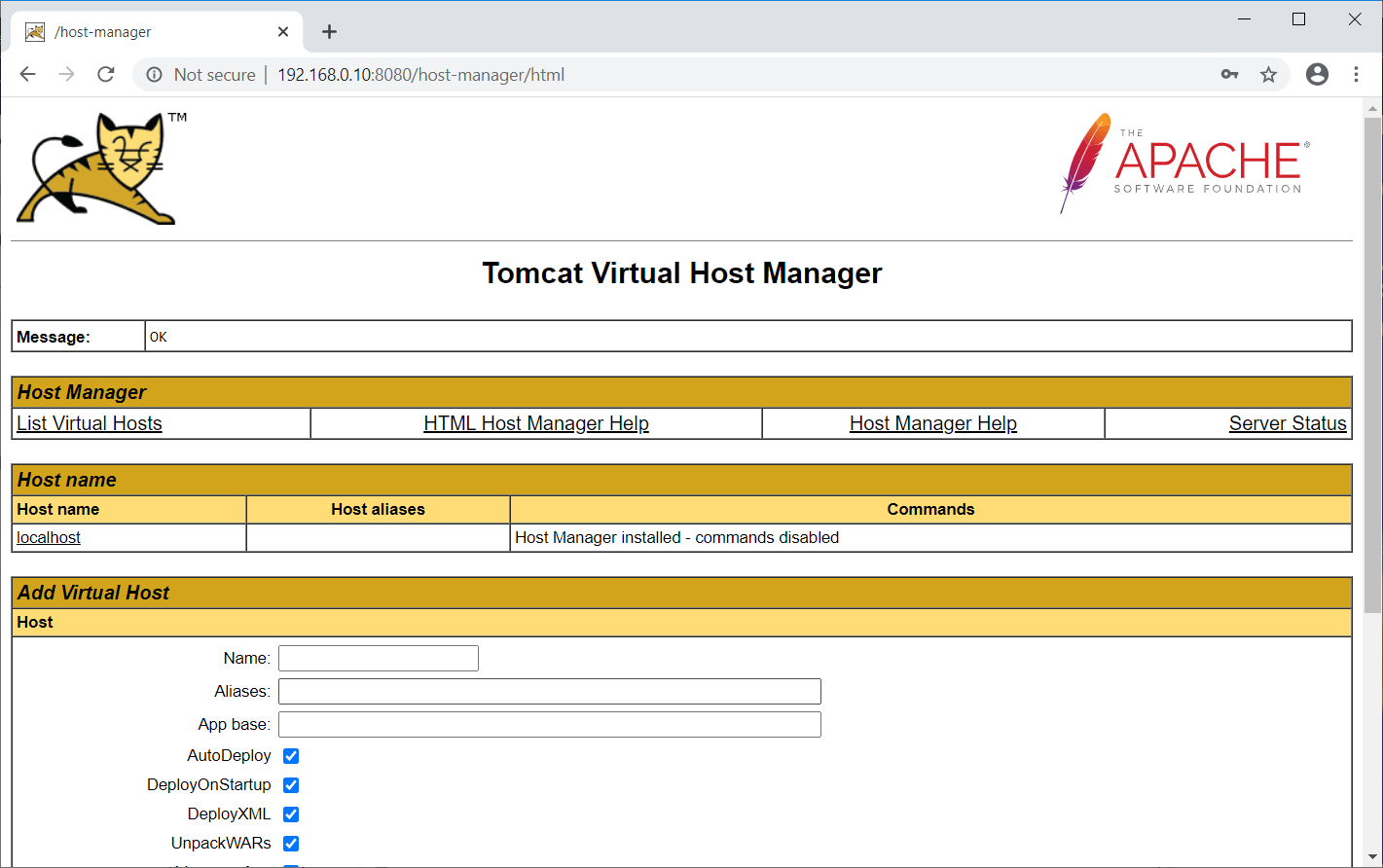
You can manage virtual hosts of Tomcat with Tomcat Virtual Host Manager by clicking on the Host Manager on Tomcat’s default page: Login Required. Username: admin, Password: password.
Conclusion
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to install Apache Tomcat on Debian 10 / Debian 9. Please share your feedback in the comments section.







![How To Upgrade To Linux Mint 20 From Linux Mint 19 [Detailed Guide]](/post/how-to-upgrade-to-linux-mint-20/featured_hu3b6c6a25dd04b6406f79faf78c8c0be6_108894_550x0_resize_q90_lanczos.jpg)