Monitor and Manage your services with Monit on CentOS 6 / RHEL 6

Monit is an opensource process tool for Linux operating system which helps you to monitor system process using web browser and also when ever requires it automatically do the maintenance or repair of particular process in such a way that it can be brought back online. It can also used for managing and monitoring of programs, files, directories, and devices for timestamps changes, checksum changes, or size changes; not limited to perform various TCP/IP network checks, protocol checks, and can utilize SSL for such checks.
It logs to its own log file and notifies the user via customizable messages, this guide will help you to setup monit on CentOS / RHEL.
Configure EPEL repo to download the latest Monit package.
[root@server ~]# rpm -Uvh https://epel.mirror.net.in/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Install the Monit.
[root@server ~]# yum -y install monit
Start monit by using the following command.
[root@server ~]# monit
Check the monit status.
[root@server ~]# monit status
The Monit daemon 5.1.1 uptime: 0m
System 'server.itzgeek.com'
status running
monitoring status monitored
load average [0.12] [0.11] [0.09]
cpu 91.6%us 8.3%sy 0.0%wa
memory usage 727512 kB [71.8%]
data collected Mon Jul 7 07:51:09 2014
Configure Monit:
Monit conig file is /etc/monit.conf, by default monit is set to check the services at interval of 2 min, this setting can be altered by changing.
[root@server ~]# vi /etc/monit.conf
set daemon 120
Alert cans be configured by.
set mailserver
Alert templates can be found in the configuration file itself.
Logs setting can be changed by using the following file.
[root@server ~]# vi /etc/monit.d/logging
set logfile
Web Interface:
Monit also provides a web interface to monitor and manage the configured services, by default monit listens on 2812 port but it needs to be setup. Open monit configuration file /etc/monit.conf.
[root@server ~]# vi /etc/monit.conf
Look for httpd port 2812, uncomment the line.
set httpd port 2812
allow 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
allow admin:admin
From the above settings, monit will listen on 2812; admin user will able to access the web interface from any network.
Reload monit.
[root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/monit restart
Access the web interface by using https://your-ip-address:2812, use the username and password mentioned in the previous step. Monit home page will look like this.
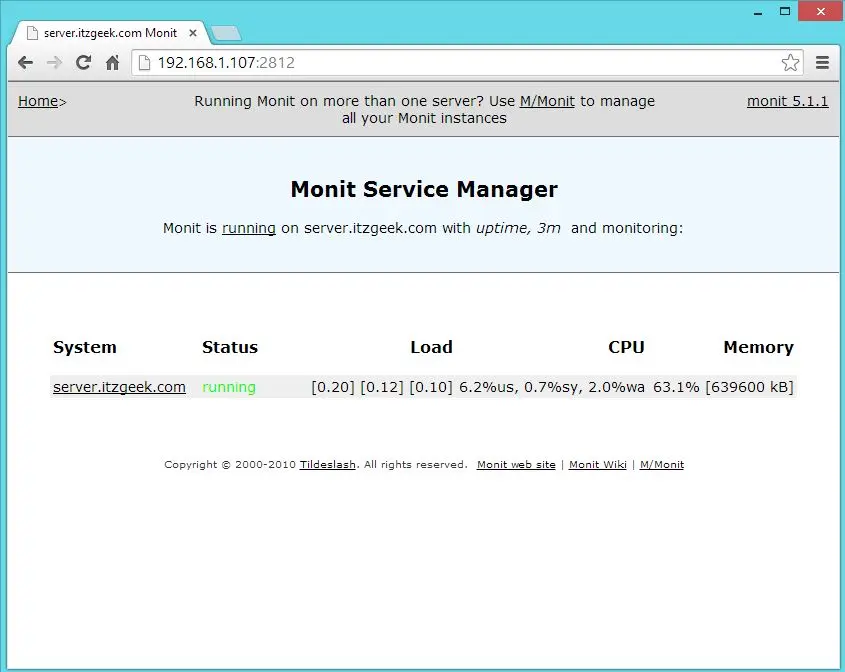
Configuring services for monitoring:
Once the web interface is up, we can start to setup other services that you want to monitor; you can place the configuration files under /etc/monit.d/ directory.
Configure for sshd.
[root@server ~]# vi /etc/monit.d/sshdmonitor
check process sshd with pidfile /var/run/sshd.pid
start program "/etc/init.d/sshd start"
stop program "/etc/init.d/sshd stop"
if failed port 22 protocol ssh then restart
Configure for syslog.
[root@server ~]# vi /etc/monit.d/syslogmonitor
check process syslogd with pidfile /var/run/syslogd.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/rsyslog start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/rsyslog stop"
Once configured, test the monit syntax
[root@server ~]# monit -t
Control file syntax OK
Reload configuration fie to take effect of changes.
[root@server ~]# monit reload
Access the web interface, you would find the new services that we configured earlier.
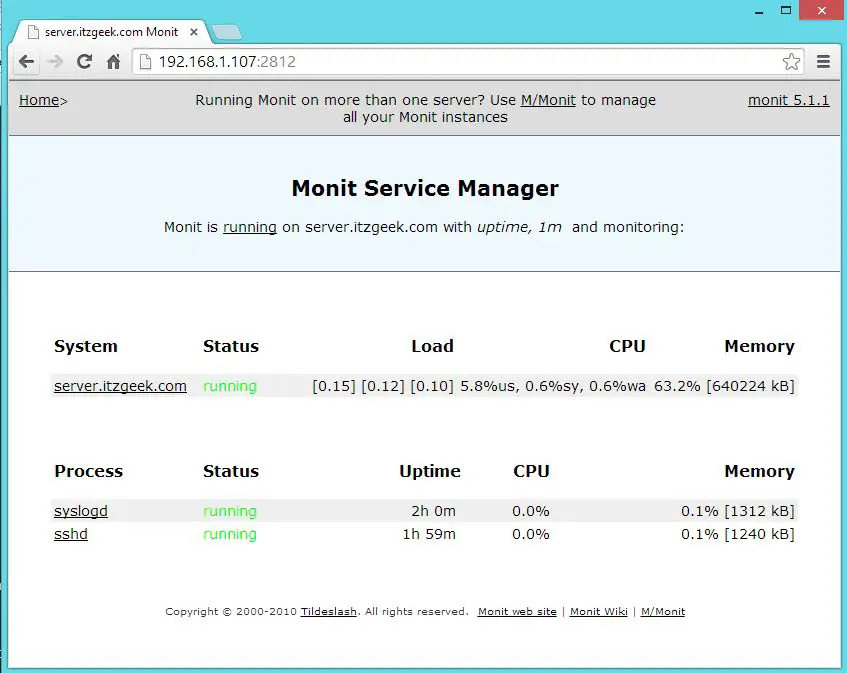
Test the Monitoring:
Now stop the syslog daemon.
[root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/rsyslog stop
Wait for 30 second, monit will start the syslog automatically. You can find it in monit log.
[root@server ~]# cat /var/log/monit
[IST Jul 7 08:50:27] error : 'syslogd' process is not running
[IST Jul 7 08:50:27] info : 'syslogd' trying to restart
[IST Jul 7 08:50:27] info : 'syslogd' start: /etc/init.d/rsyslog
[IST Jul 7 08:51:28] info : 'syslogd' process is running with pid
That’s All, We have successfully configured Monit on CentOS 6 / RHEL 6. We welcome your feedback, please post your valuable comments below.
