How To Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
Cockpit is a free software which provides a web-based interface for the system admin to perform tasks, such as starting containers, storage management, network configuration, inspecting logs and so on.
Cockpit is released under the LGPL v2.1+; it is available for Debian, Redhat, CentOS, Atomic, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu.
This guide focuses on installing Cockpit on Ubuntu 16.04.
Features
- Connect and Manage multiple machines from a single Cockpit session
- Manage the containers via Docker
- Modify the network settings
- Easily manage the user accounts
- Provides web-based shell in a terminal
- Gathers system performance using Performance Co-Pilot framework and displays it in a graph.
- With the use of sosreport, it can collect system configuration and diagnostic information
- It can interact with a Kubernetes cluster or an Openshift v3 cluster
Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 16.04
/etc/apt/sources.list file.deb https://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Update the apt database.
sudo apt-get update
Install the Cockpit package.
sudo apt-get -y install cockpit
Working with Cockpit
Once you start the Cockpit service, it will start to listen on port 9090. You can open up your favorite browser and navigate it to below URL.
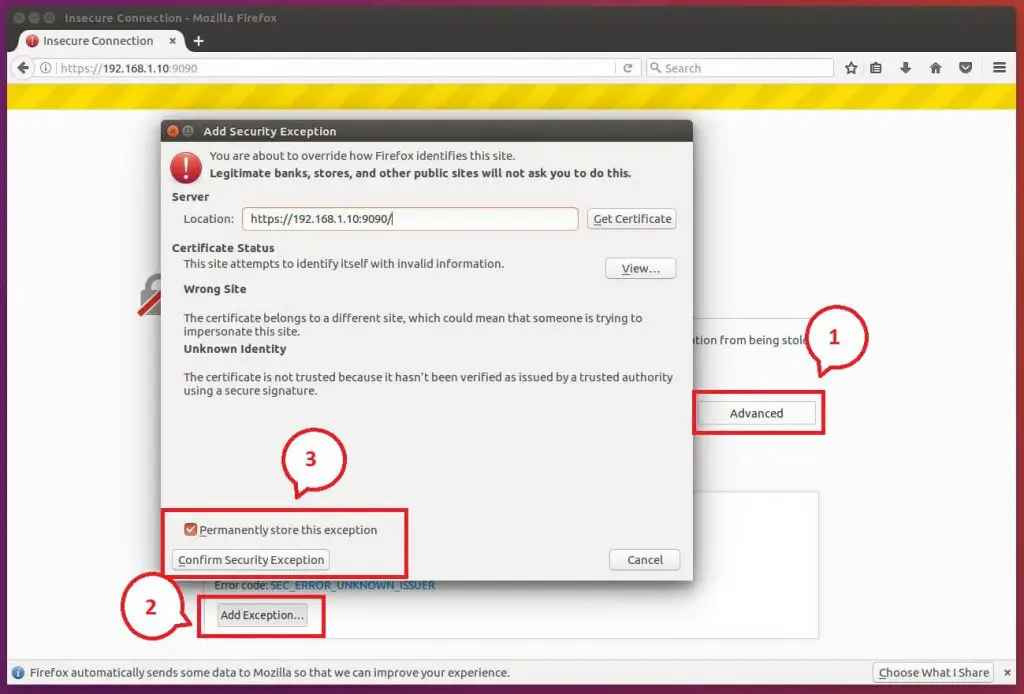
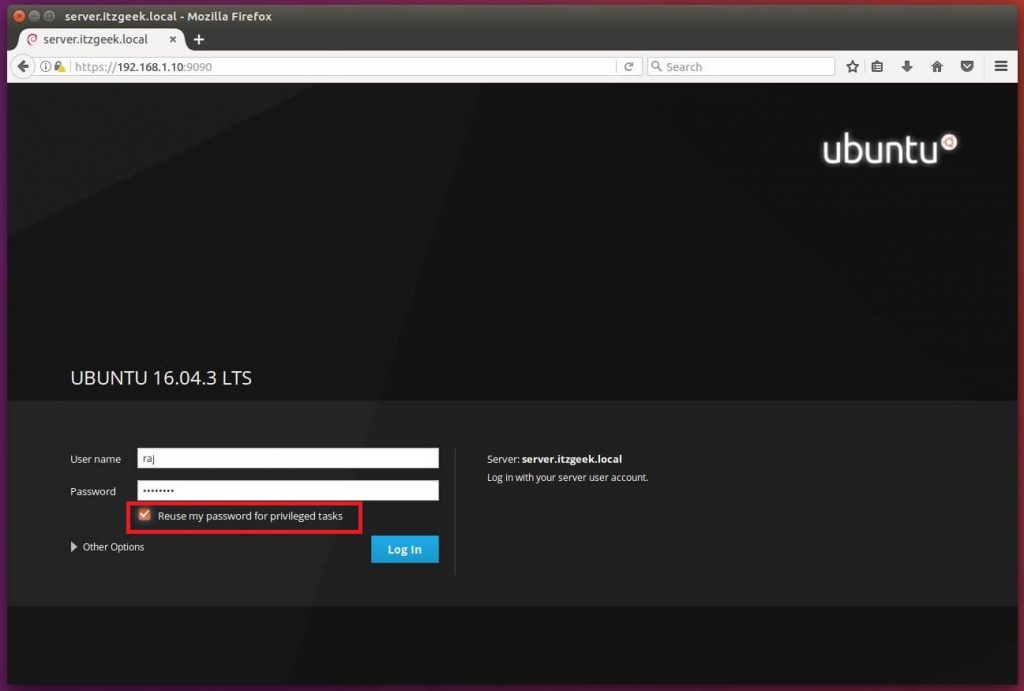
Log in with your local user account. In my case, it is “raj”.
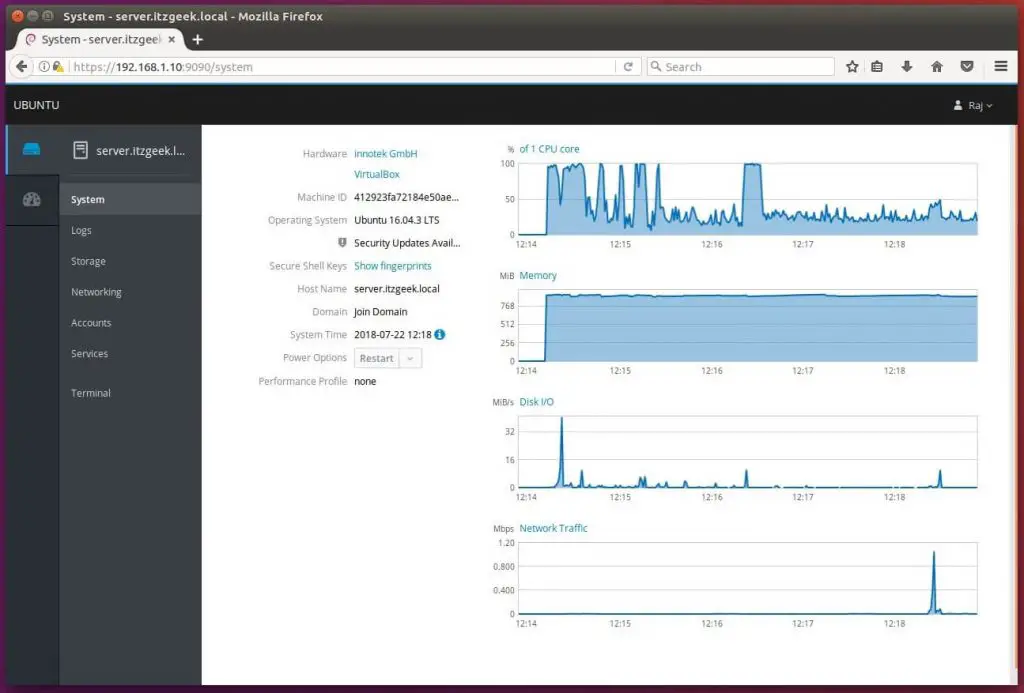
Once you have logged in, it will take you to the system overview page where you can have a detailed overview and performance graphs of the selected system.
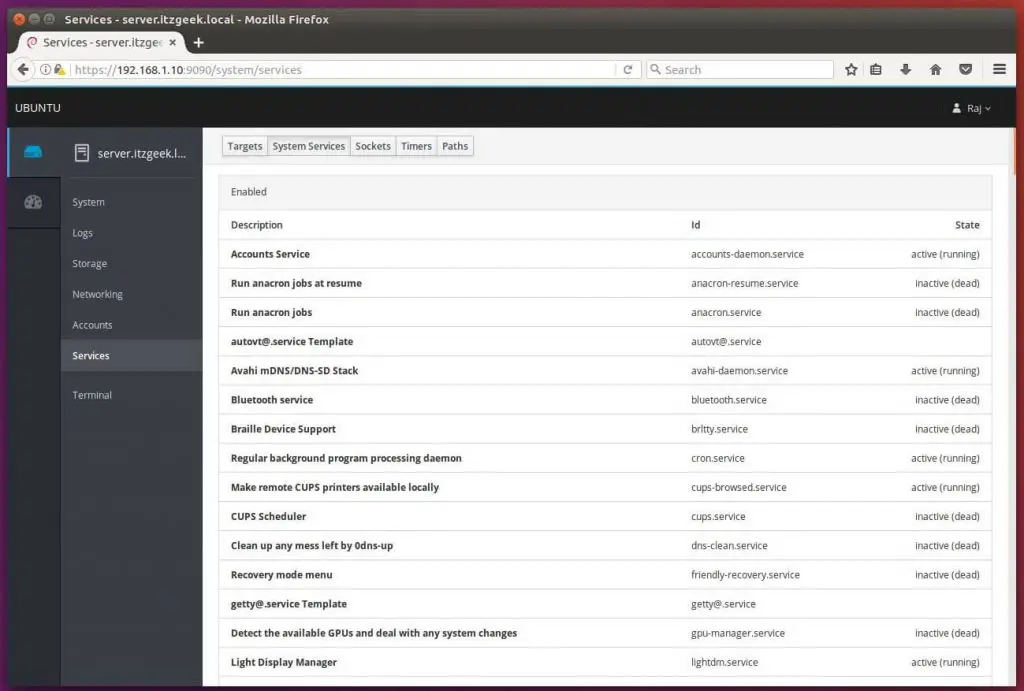
You can take a look at the details of running services by clicking on the services page; here, you can manage (start, stop, restart, etc.look) the services by clicking on particular service.
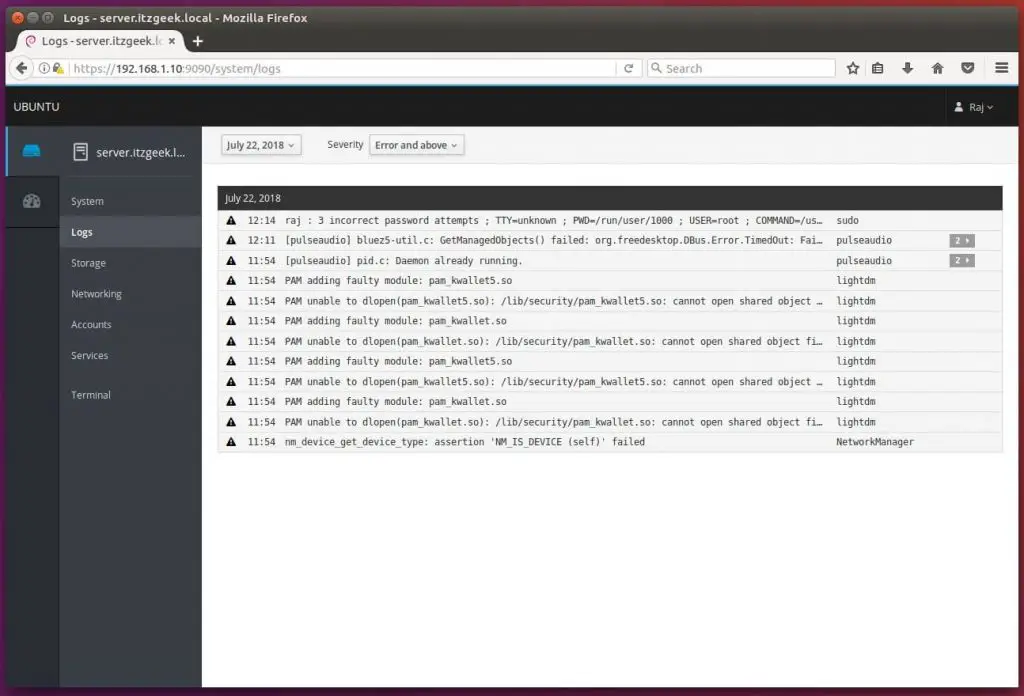
Troubleshoot your machine by having a look at the system logs.
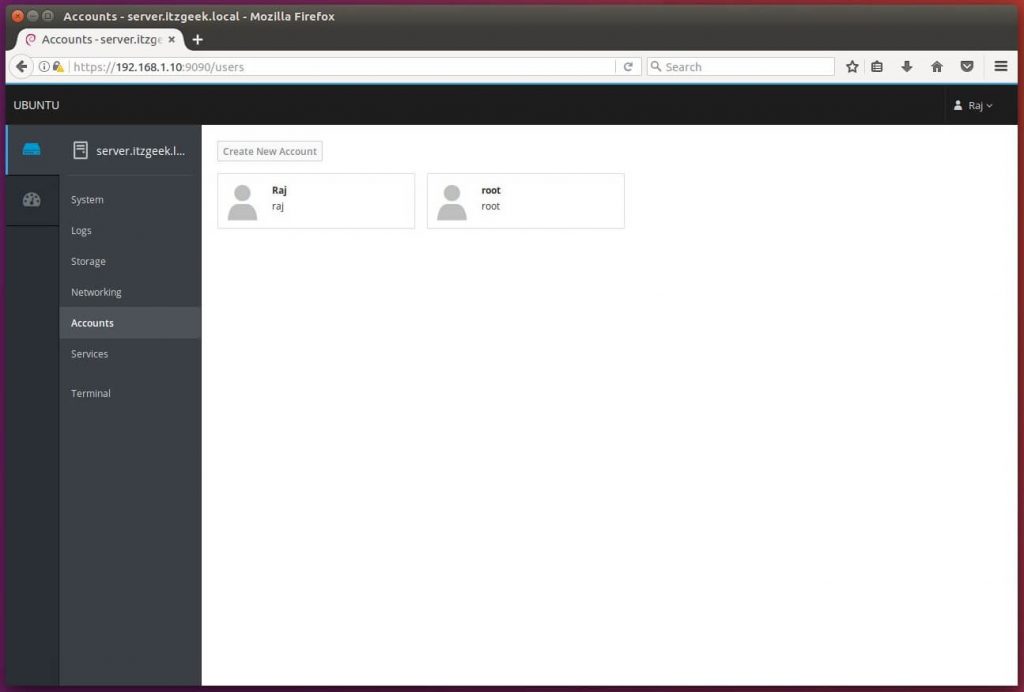
Manage the system users by going to Accounts
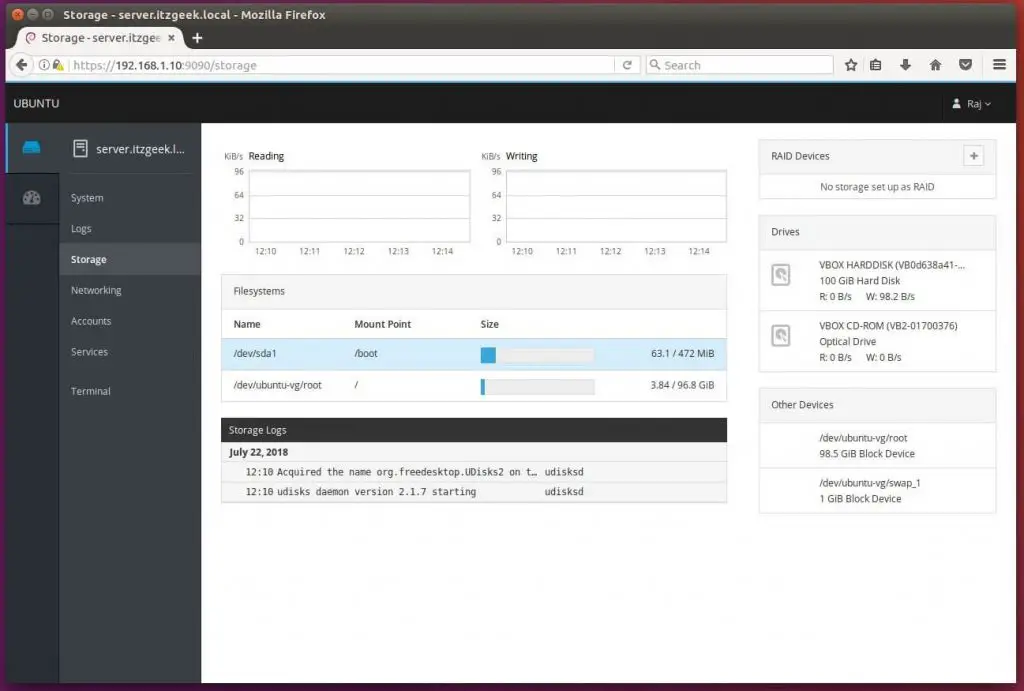
You can also manage system storage with Cockpit.
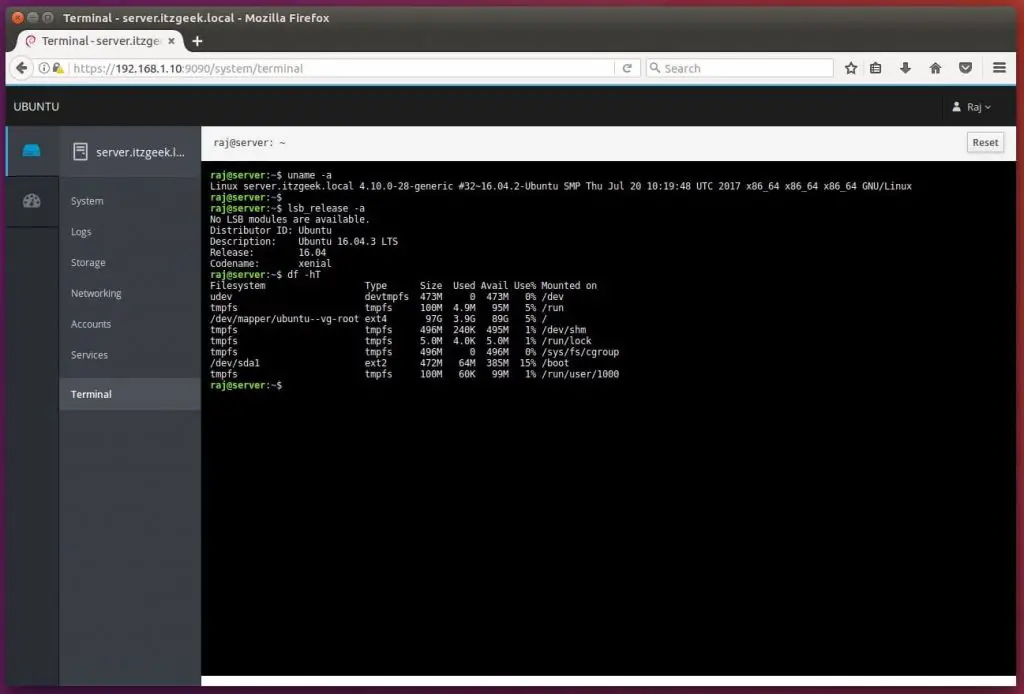
If you are looking to take terminal of the server, you no need to take putty and work. Just click Terminal.
Manage Multiple Servers with Cockpit
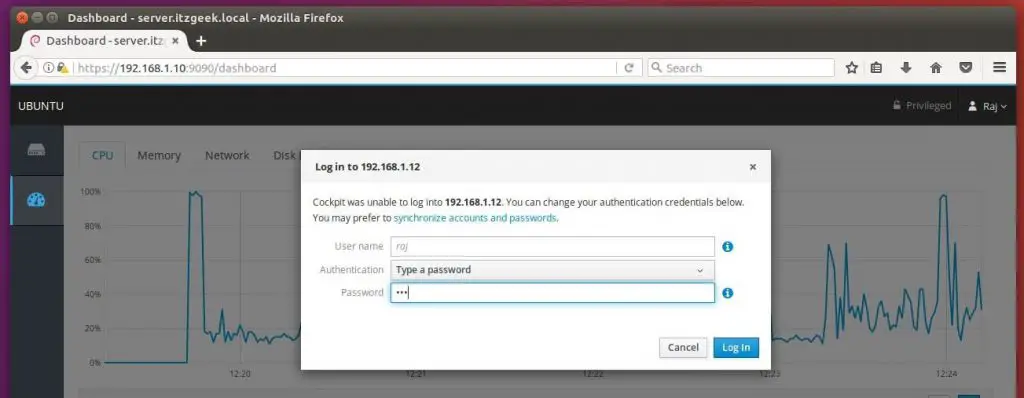
Consider if you have multiple servers with Cockpit and want to manage them in a single session. Click on Dashboard and then click the Plus sign icon and add them one by one.
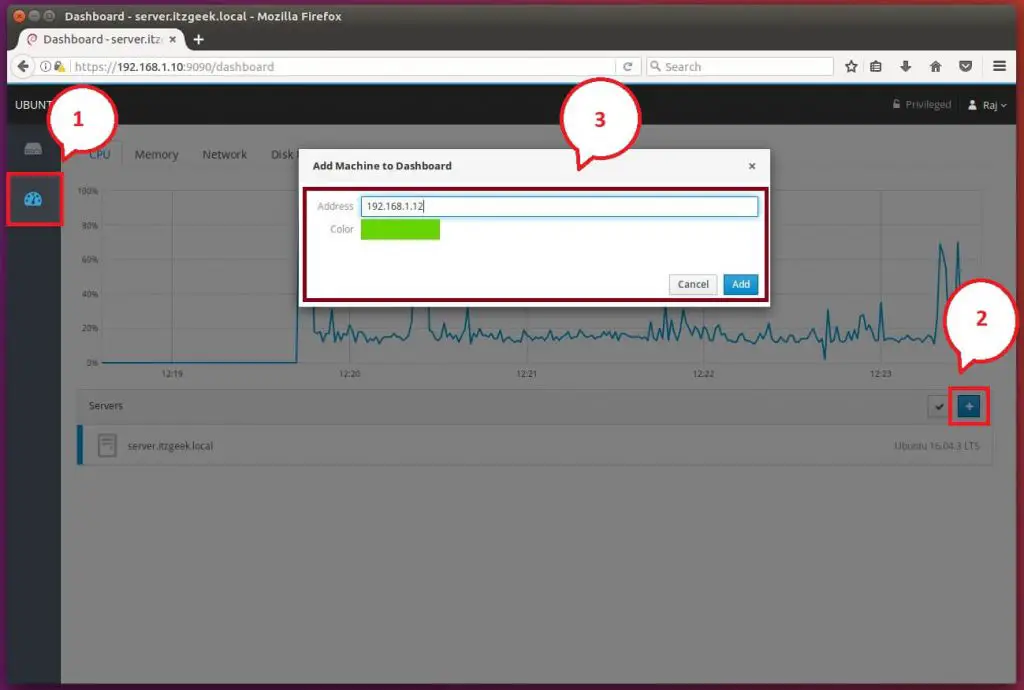
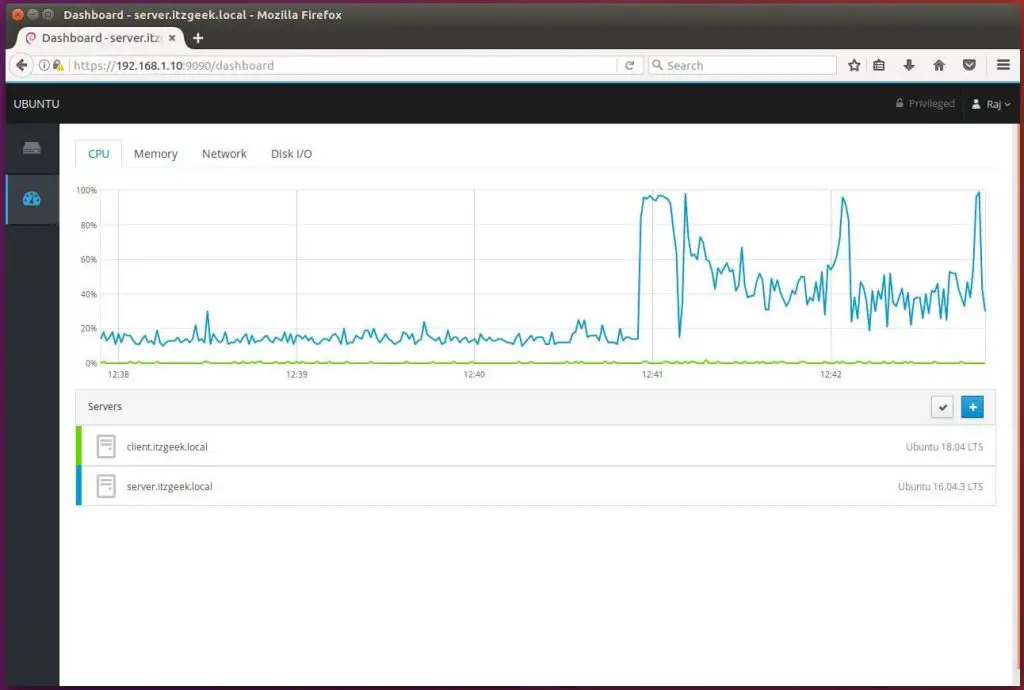
Below screenshot shows that two machines are attached to this Cockpit session.
server.itzgeek.local (Ubuntu 16.04 – Local Machine)
client.itzgeek.local (Ubuntu 18.04 – Remote Machine)
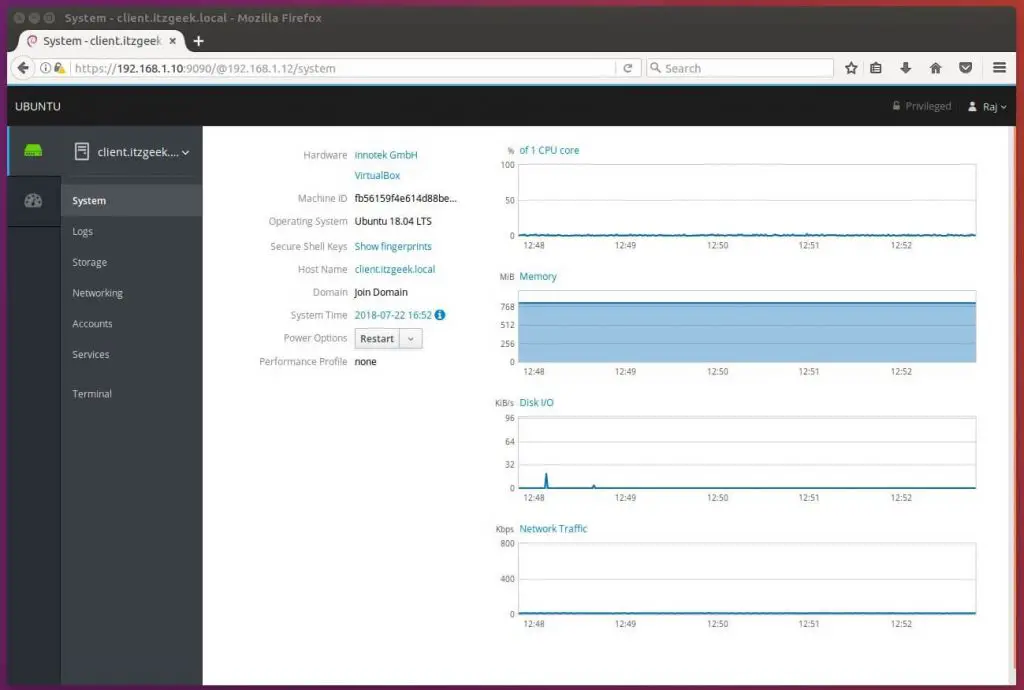
Below screenshot shows the detailed information of the remote system.
That’s All.
