How To Install Cockpit on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Cockpit is a web-based administration tool for the system admin to manage and monitor the local system, as well as the remote Linux servers in your infrastructure.
The Cockpit console lets you perform a wide range of administration tasks, including:
- Manage remote machines in a single Cockpit console
- Manage Podman containers
- Modify Network interfaces
- Manage Virtual Machines
- Manage user accounts
- Web-based terminal
- View system performance in a graph.
- Collect system configuration and diagnostic information with the use of sosreport.
Here, we will see how to install Cockpit on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
Install Cockpit
CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 includes the Cockpit installed by default during the OS installation except for the minimal installation.
Install the Cockpit package in case the package is not already installed.
dnf install -y cockpit
You can install add-on packages to manage other tasks using Cockpit.
Enable the Cockpit service.
systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Firewall
Add a firewall rule to allow Cockpit to manage the remote machines as well as to enable us to access the Cockpit dashboard from external machines.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=cockpit
firewall-cmd --reload
Access Cockpit
The Cockpit console should now be accessible if you visit the below URL using the browser.
Click proceed if you get a warning message for a self-signed certificate and proceed to access the Cockpit console.
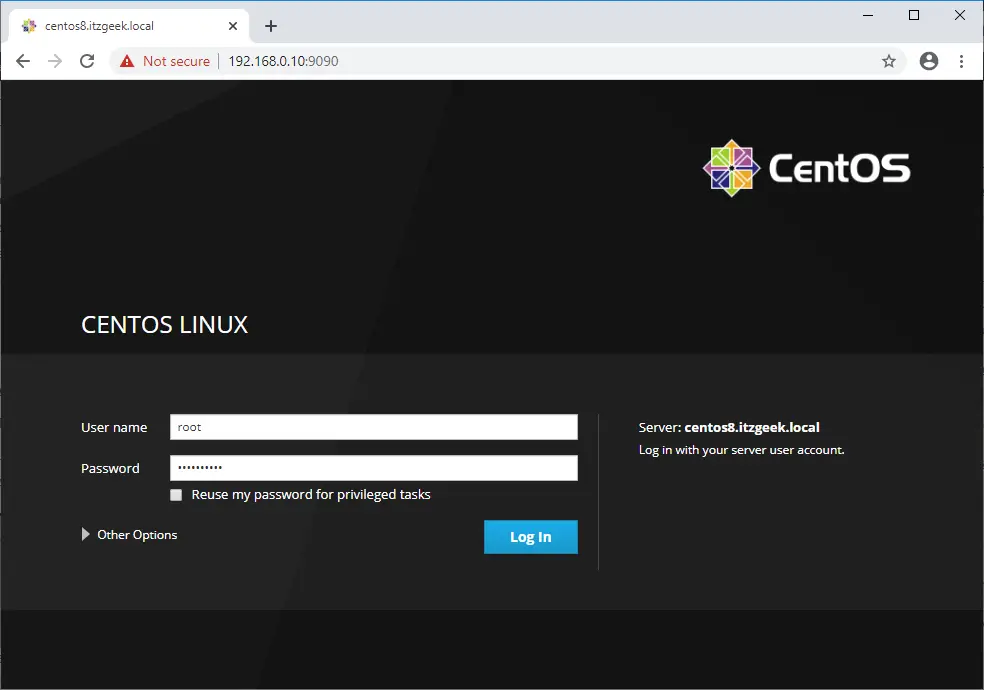
Log in to Cockpit with your local system user account. In my case, it is root.
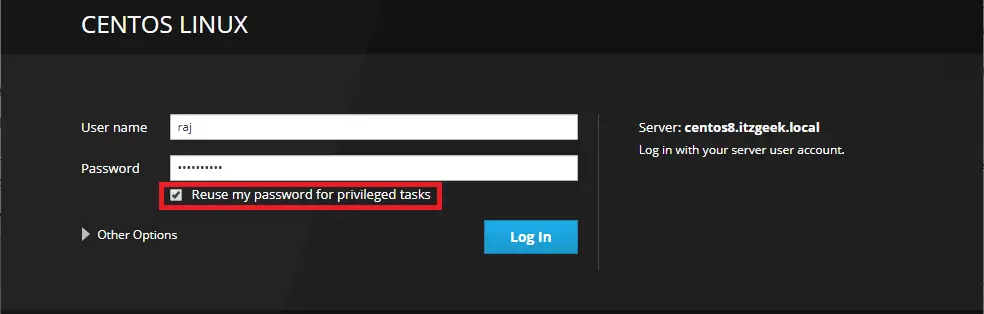
Working With Cockpit
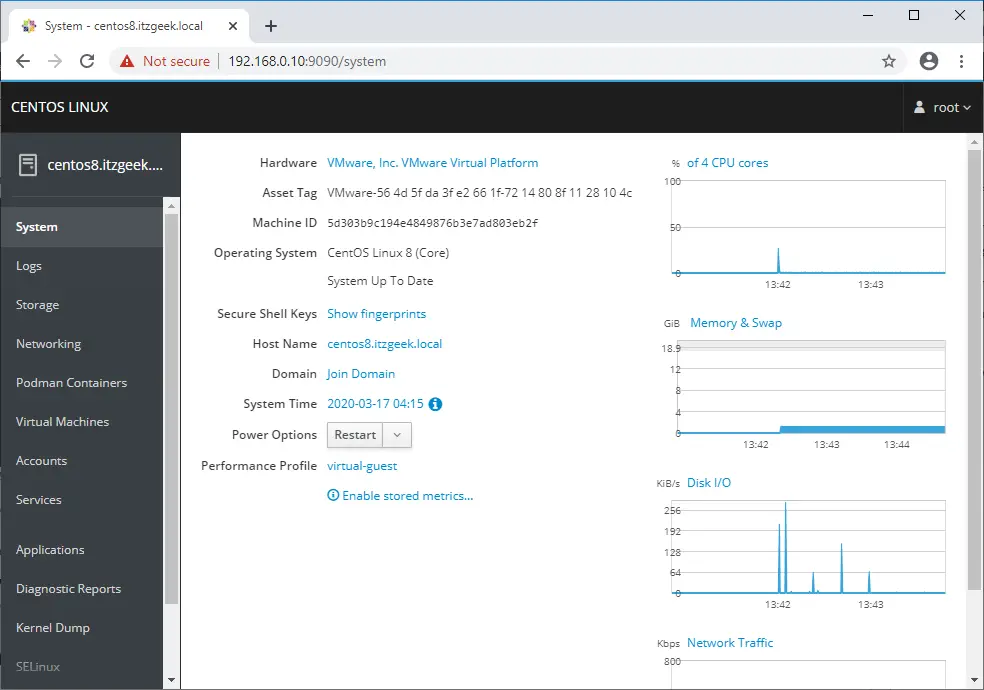
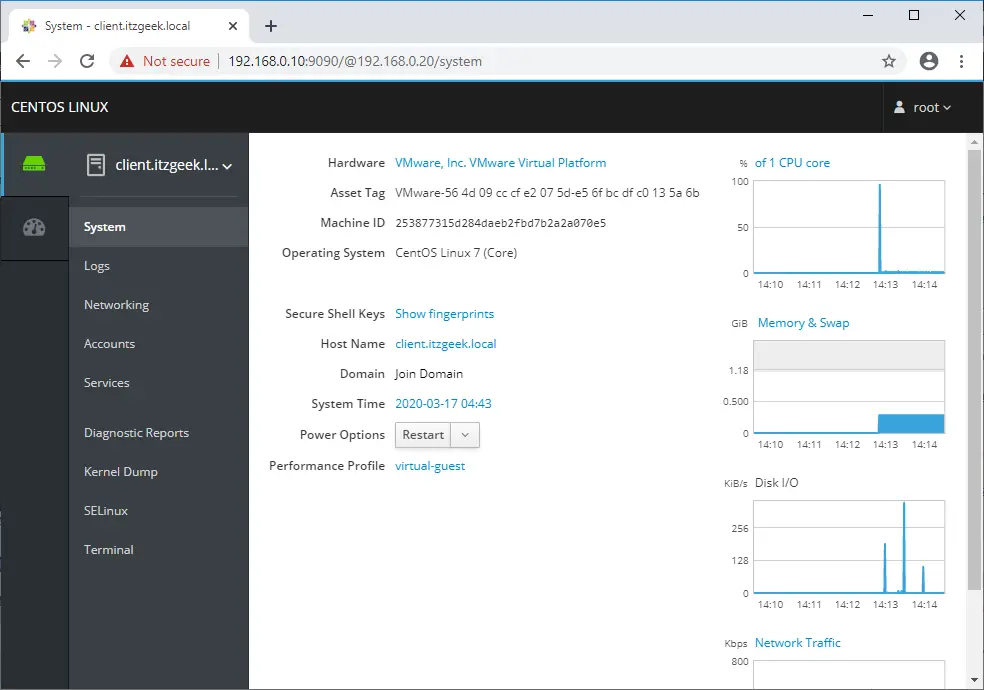
Once you have logged in into the Cockpit console, you will get the System page where you can see an overview of your system. Here, you can change the hostname, time, restart or shut down the system and view the system usage graphs.
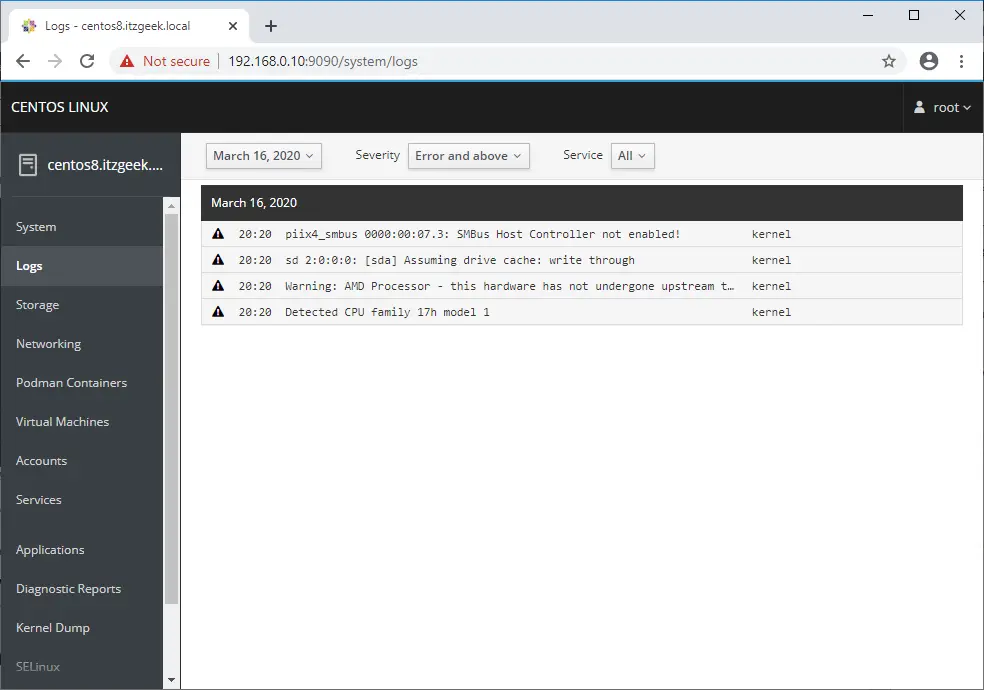
You can view logs from the console to troubleshoot your system issues. You have an option to filter the logs based on duration and severity.
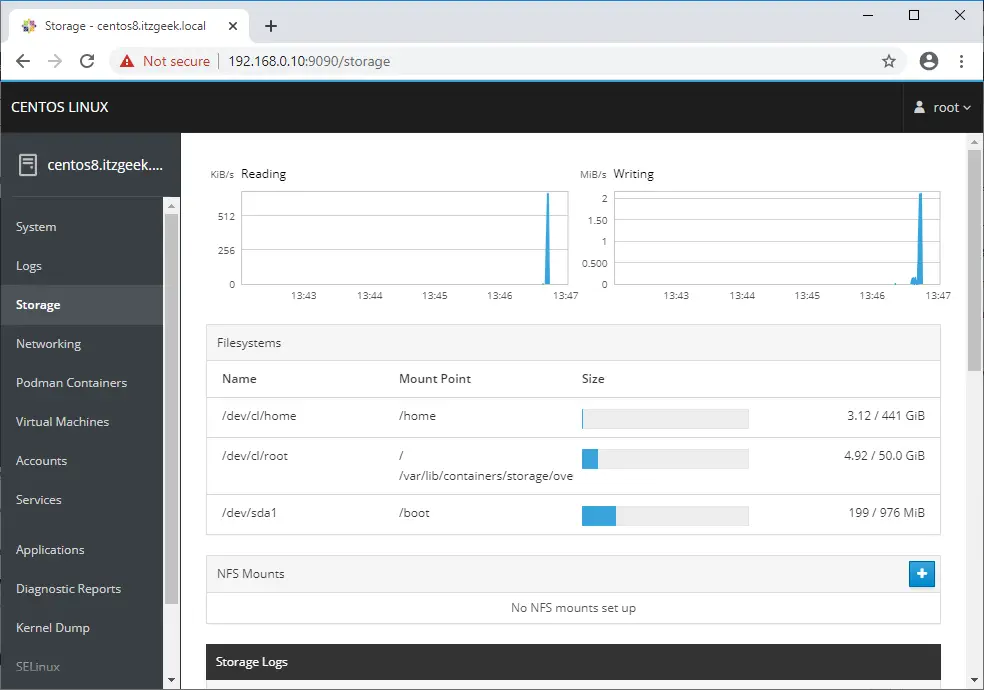
You can manage disks, partitions, and LVM by going to Storage (dnf install -y cockpit-storaged). Also, you can check disk read and write performance and storage logs.
Another important section is Networking. Here, you can change the system IP address, create network bonding, teaming, network bridge and add VLAN. In addition to that, you can manage the firewall and view the network graphs and logs.
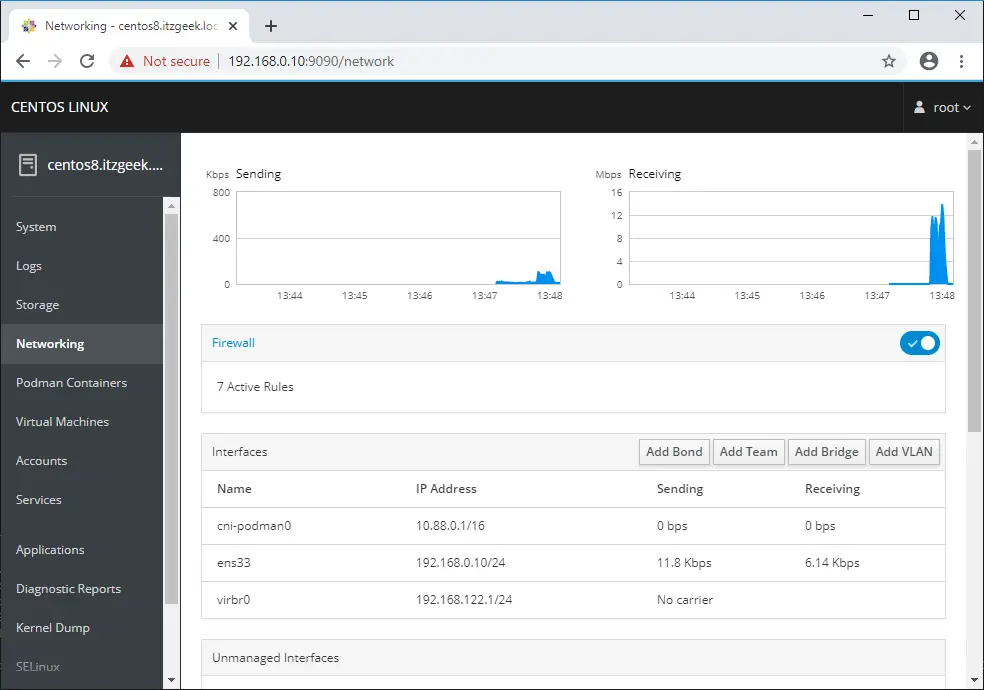
You can manage Podman containers by going yo the Podman Containers (dnf install -y cockpit-podman) page. Here, you can run, stop, delete and commit containers.
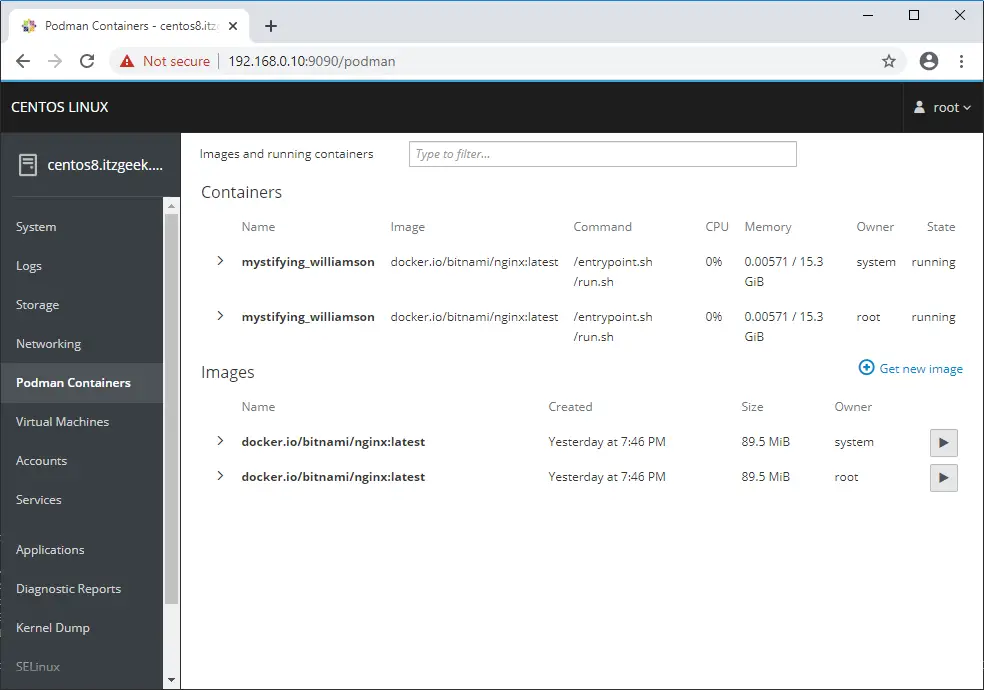
Manage the Kernel virtual machines (dnf install -y cockpit-machines) by going to Virtual Machines.
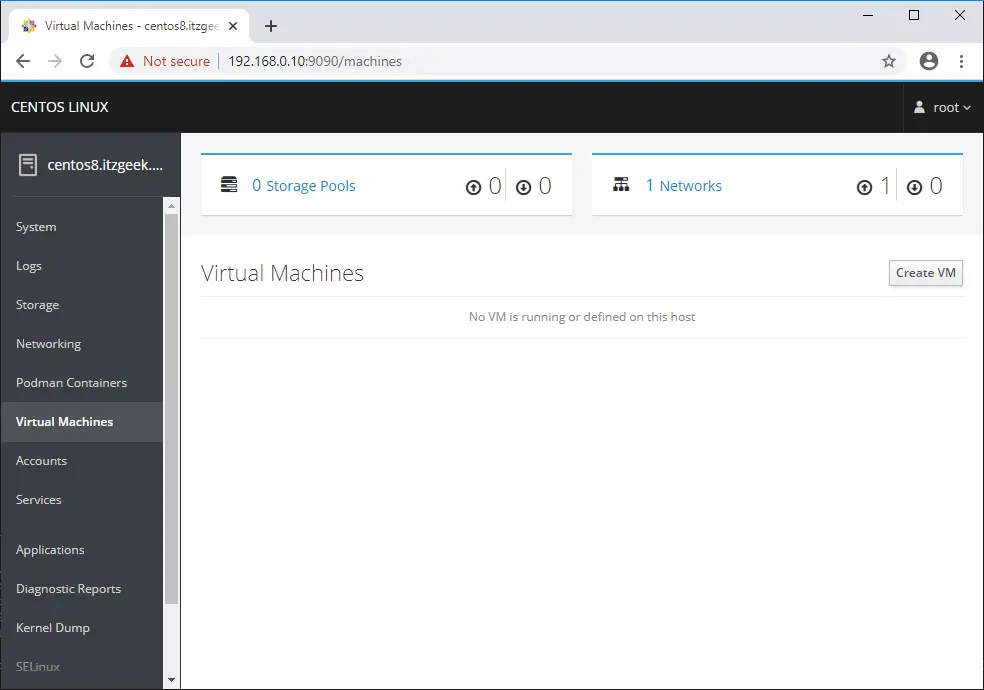
You can create and manage the system users by going to Accounts.
You can see the details of system services by clicking on Services. Here, you can start, stop, restart, enable or disable the service by clicking on a particular service.
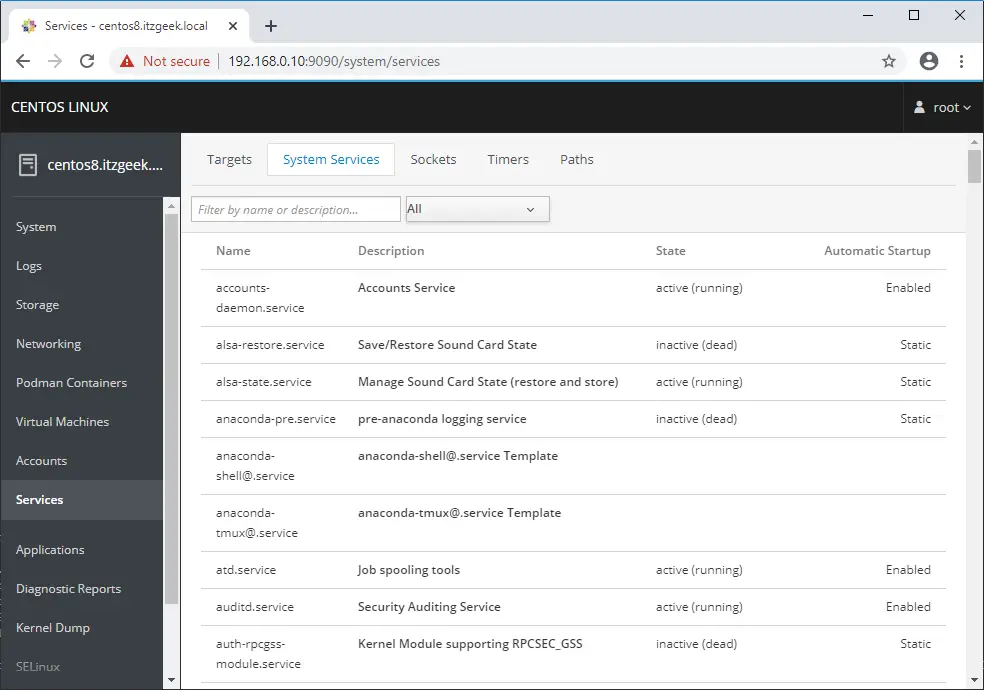
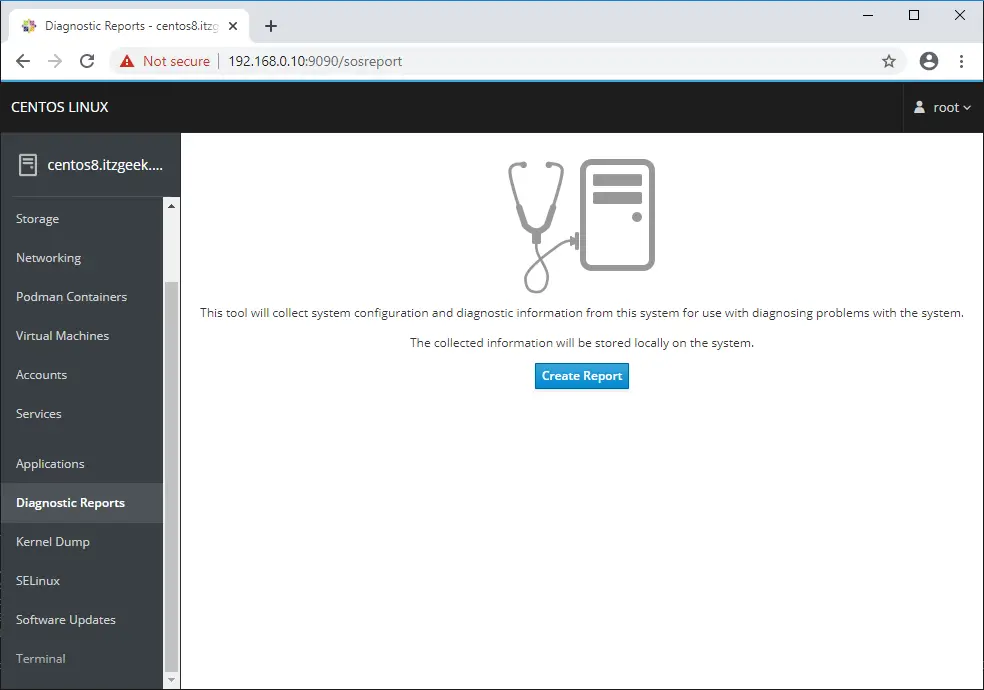
You have an option to generate a sosreport and share it with the support team by going to Diagnostic Reports using the Cockpit.
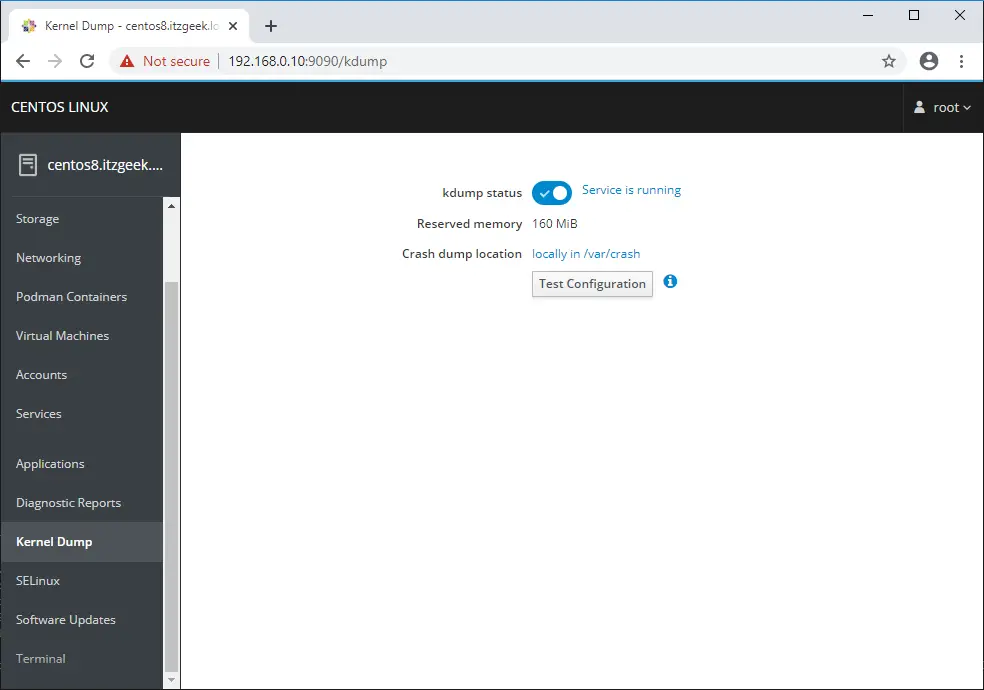
Manage kernel crash dump by going to Kernel Dump. You can also test kernel crash dump configuration.
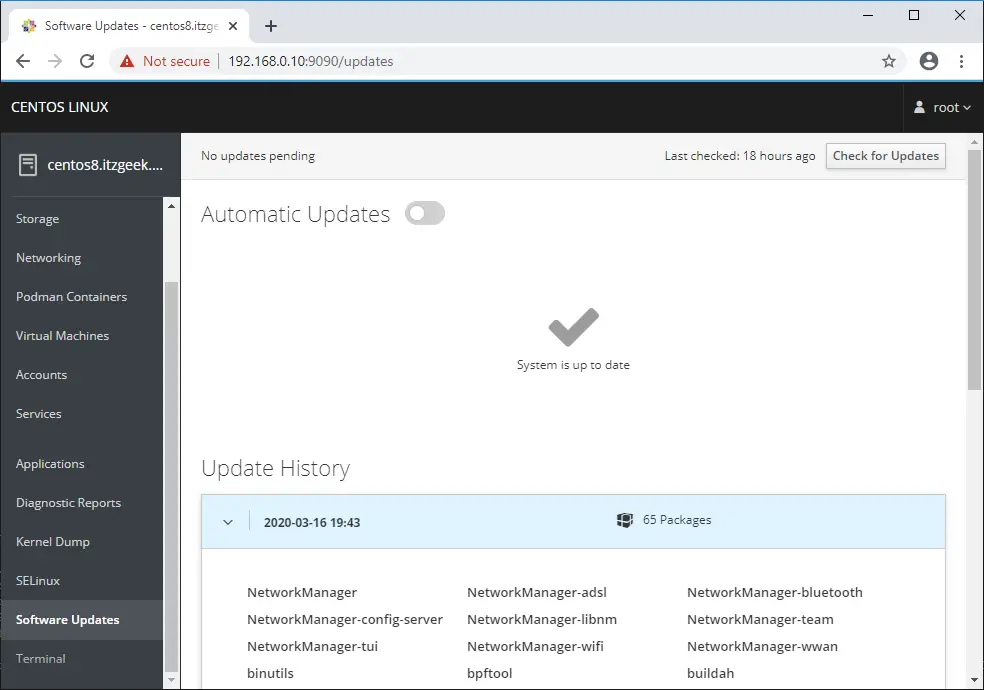
You can seamlessly update the system packages using Software Updates.
You can also take the terminal of the server by clicking on the Terminal.
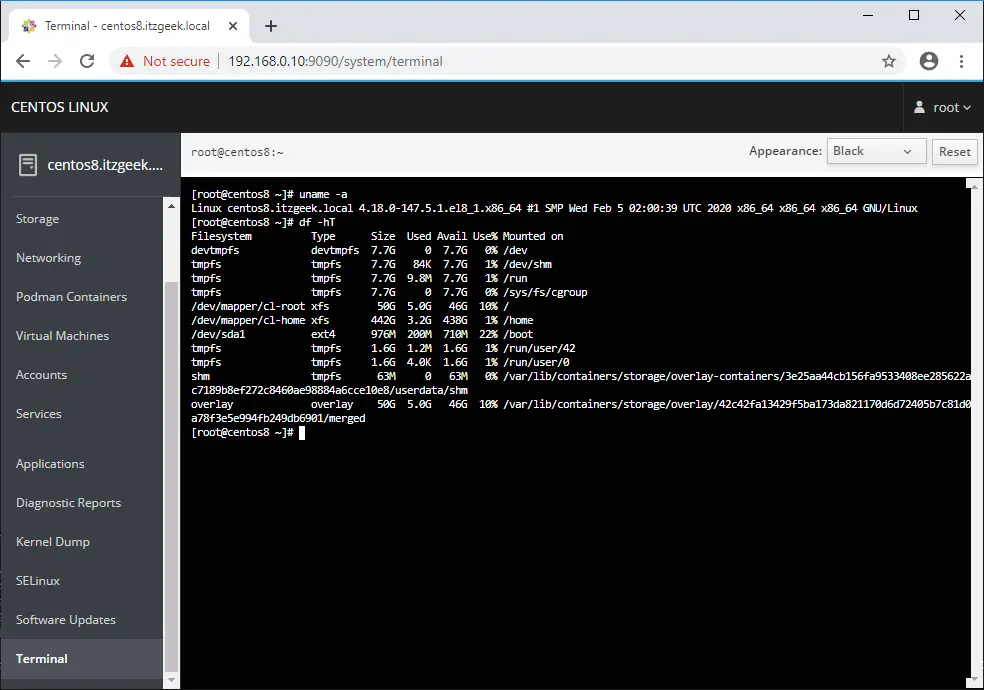
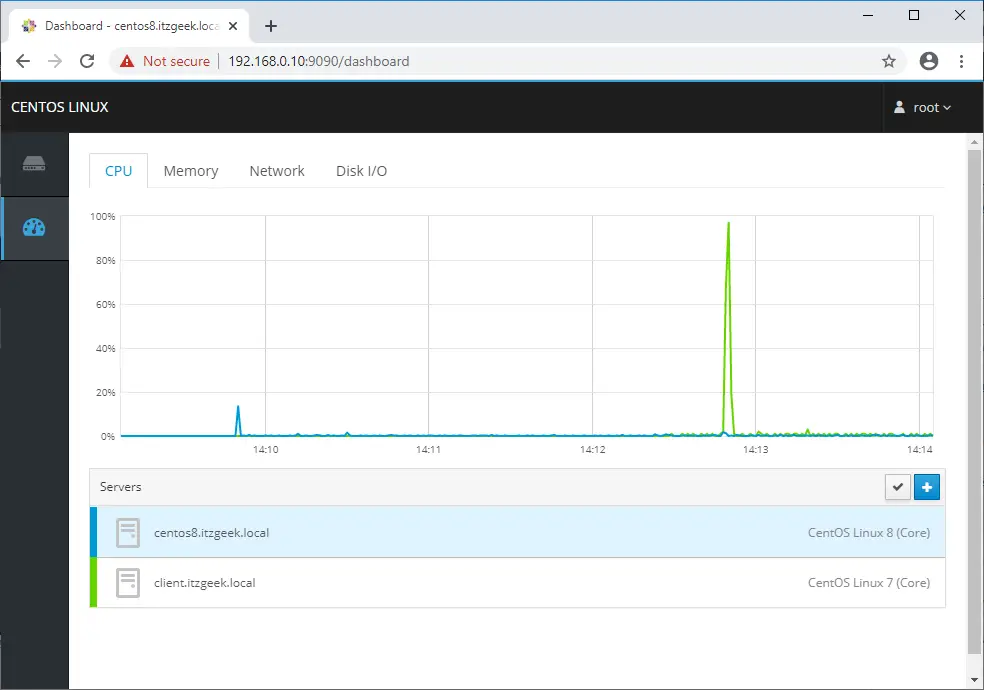
Manage Multiple Servers with Cockpit
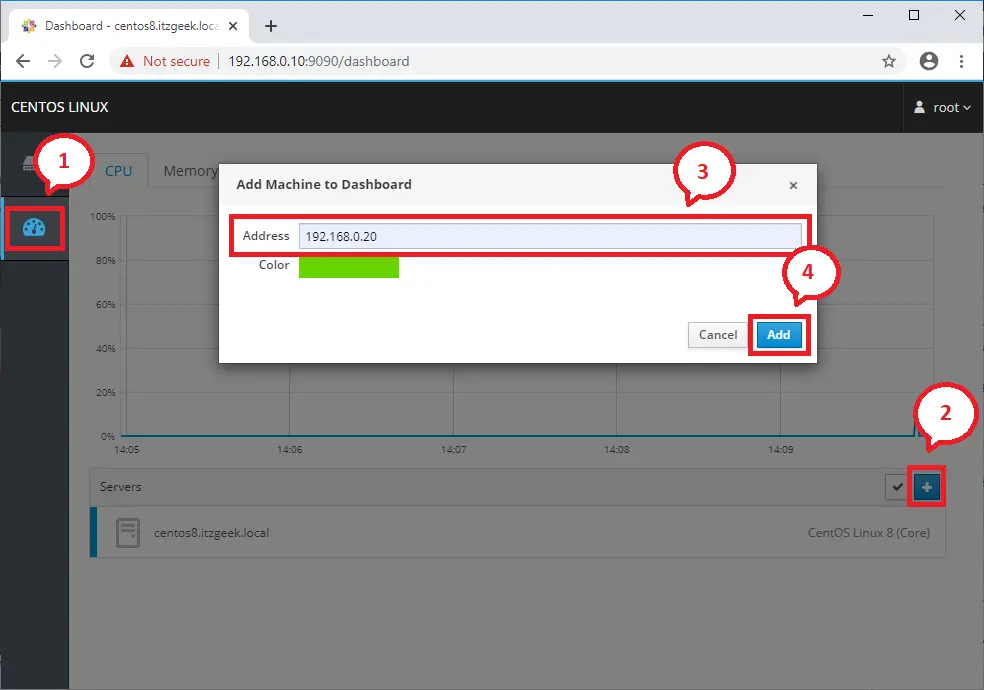
To add a remote server with Cockpit, click on Dashboard (dnf install -y cockpit-dashboard && systemctl restart cockpit.socket). Then, click on the Plus sign icon to add it.
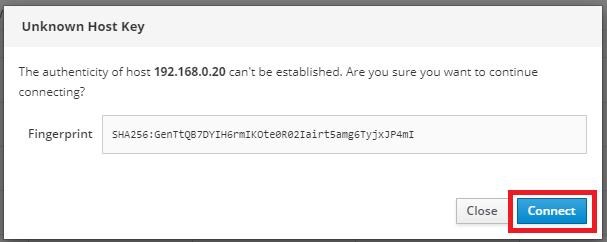
Click connect when Cockpit reports Unknown Host Key.
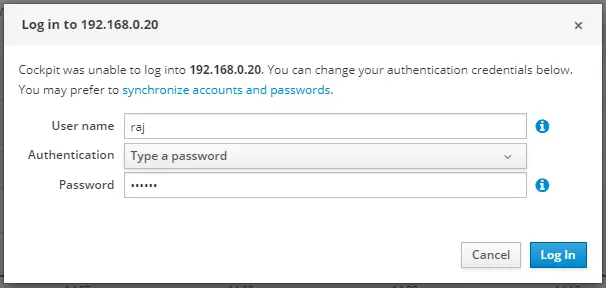
You should now see the local and remote machine(s) in the Cockpit dashboard.
Overview of the remote system:
Conclusion
That’s All. I hope you have learned how to install Cockpit on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 and use it for system administration activities.








![How To Upgrade To Linux Mint 20 From Linux Mint 19 [Detailed Guide]](/post/how-to-upgrade-to-linux-mint-20/featured_hu3b6c6a25dd04b6406f79faf78c8c0be6_108894_550x0_resize_q90_lanczos.jpg)